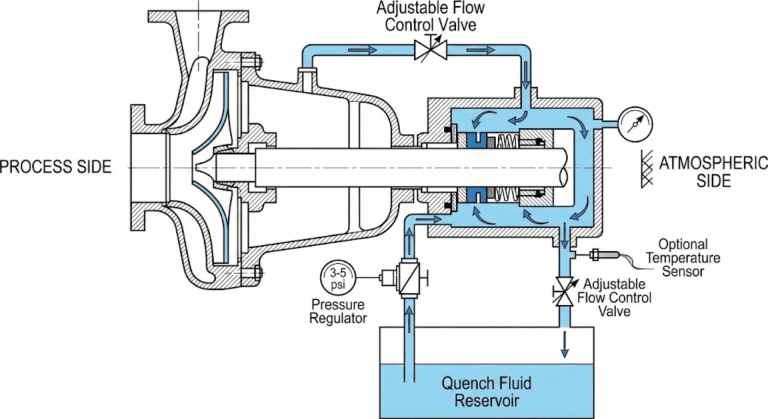
You are replacing a 기계식 씰 O-ring and the parts catalog lists two elastomer options: FKM and EPDM. Both are premium materials with excellent service life. Choose wrong, however, and that seal could fail within weeks.
The difference matters because these materials have nearly opposite strengths. FKM resists oils and handles high temperatures. EPDM excels in water, steam, and cold environments. Matching the elastomer to your operating conditions prevents premature failure and unnecessary replacement costs.
This guide provides a clear decision framework based on fluid type, temperature range, and application requirements. By the end, you will know exactly which elastomer to specify for your mechanical seal.
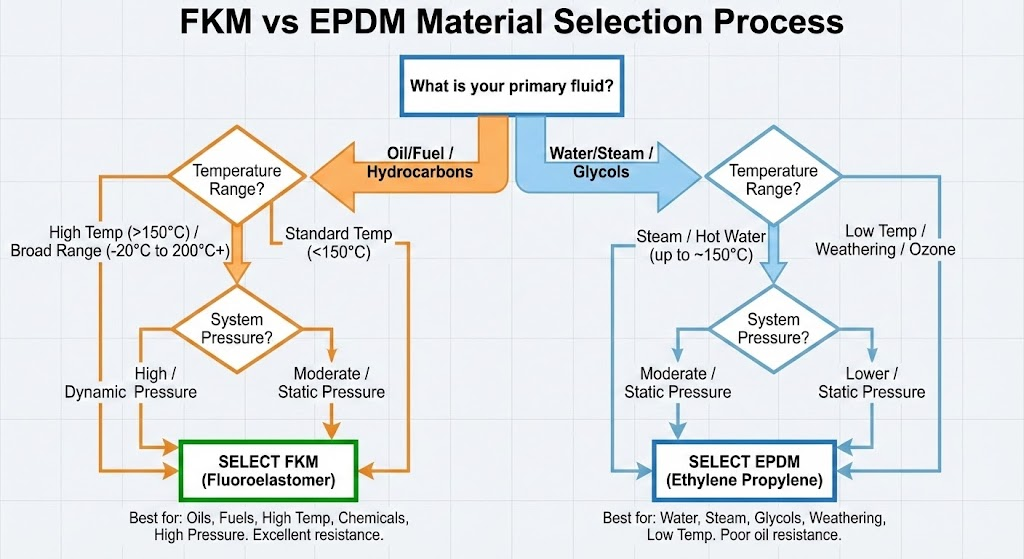
Which Elastomer Material Should You Choose: FKM or EPDM?
Choose FKM when your application involves oils, fuels, or continuous temperatures above 150C. Choose EPDM for water, steam, brake fluid, or sub-zero environments. This single decision rule covers most mechanical seal applications.
Quick Selection Guide
| Application | Recommended | Why |
|---|---|---|
| Hot water / Steam | EPDM | FKM degrades via hydrolysis |
| Petroleum oils and fuels | FKM | EPDM swells and fails |
| Brake systems (DOT 3/4) | EPDM | Industry standard; FKM incompatible |
| High temperature (>150C) | FKM | EPDM max is 150C |
| Sub-zero cold (-40C) | EPDM or FKM GLT | Standard FKM only to -20C |
| Outdoor/UV exposure | EPDM | Excellent ozone/UV resistance |
| Aggressive chemicals | FKM (GF grade) | 70% fluorine content |
| Food & beverage (water-based) | EPDM | FDA grades available |
| HVAC systems | EPDM | Water resistant; cost-effective |
The Key Difference in One Sentence
FKM is the chemical and oil resistance champion. EPDM is the water, steam, and cold environment specialist.
The fluorine atoms in FKM create strong carbon-fluorine bonds that resist petroleum products and most chemicals. EPDM’s ethylene-propylene backbone provides exceptional stability in water-based environments where FKM would degrade.
What Are the Key Property Differences Between FKM and EPDM?
FKM handles higher temperatures and pressures. EPDM offers better flexibility in cold conditions and superior tear resistance. These mechanical differences often determine which material suits your pump application.
Temperature Performance Comparison
| Property | FKM | EPDM |
|---|---|---|
| Standard range | -26C to +205C | -40C to +150C |
| Low-temperature limit | -20C (GLT grade to -40C) | -50C |
| High-temperature limit | 250C continuous, 300C intermittent | 150C (steam grades to 200C) |
| 최적 용도 | Continuous high-heat operation | Cold starts and sub-zero environments |
FKM is serviceable in continuous heat of up to 250C and intermittent heat of up to 300C. This makes it the clear choice for applications like hot oil systems and high-temperature chemical processes.
EPDM operates reliably at temperatures as low as -50C. For cold climate installations or cryogenic adjacent equipment, EPDM maintains flexibility where standard FKM would become brittle.
Mechanical Properties
| Property | FKM | EPDM |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Shore A) | 75-90 | 70-80 |
| Max Pressure | 3,000 PSI | 1,500 PSI |
| Compression Set | 우수함 | 양호함 |
| Tear Resistance | 양호함 | 우수함 |
| Abrasion Resistance | 양호함 | 우수함 |
FKM’s higher hardness and pressure rating make it suitable for high-pressure pump applications. I recommend FKM for any system operating above 1,500 PSI.
EPDM’s superior tear resistance and elongation at break (300% to 600%) make it more forgiving during installation. This matters for maintenance teams handling frequent seal changes.
Chemical Resistance Overview
| Chemical Category | FKM Rating | EPDM Rating |
|---|---|---|
| Petroleum oils | 우수함 | Poor – swells |
| Fuels/Gasoline | 우수함 | Poor – fails |
| Hot water/Steam | Poor – degrades | 우수함 |
| Ketones/Acetone | Poor | 우수함 |
| Brake fluid (DOT 3/4) | Fails | 우수함 |
| Acids (dilute) | 우수함 | 양호함 |
| Ozone/UV | 우수함 | 우수함 |
| Alcohols | Good to Excellent | 양호함 |
The compatibility table reveals a critical pattern: where FKM excels, EPDM fails, and vice versa. This is why specifying the wrong elastomer causes rapid 씰 고장 rather than gradual wear.
Why Does FKM Fail in Water and Steam Applications?
FKM fails in hot water and steam because of hydrolysis – a chemical attack that breaks down the polymer structure. This is not a quality issue or manufacturing defect. It is fundamental chemistry.
The Hydrolysis Mechanism
As one engineer on Eng-Tips explained: “The hot water has a relatively high concentration of OH- radicals, which tend to attack crosslinks both between and along the polymer chain.”
This mechanism means standard FKM seals in steam service will degrade regardless of brand or quality. The OH- radicals cause chain scission, breaking the polymer into shorter segments. The seal loses elasticity, develops cracks, and eventually fails.
For water, steam, and brake fluid applications, EPDM is not just acceptable – it is the only correct choice. Using FKM in these conditions leads to premature failure that no amount of seal quality can prevent.
When EPDM Is the Only Correct Choice
EPDM should be specified for:
- Hot water service above 60C
- Steam environments up to 200C
- Brake systems using DOT 3 or DOT 4 fluid
- HVAC and water treatment systems
- Boiler feed applications
- Condensate return lines
O-rings with EPDM as the base polymer reliably retain their properties even when exposed to hot water and steam at temperatures of up to 200C. No other common elastomer matches this performance in water-based environments.
The Peroxide-Cured FKM Exception
Peroxide-cured FKM offers improved resistance to steam compared to standard bisphenol-cured FKM. Engineers recommend this variant when an application requires both chemical resistance and occasional steam exposure.
However, peroxide-cured FKM still does not match EPDM’s water resistance. Consider it only when you need FKM’s chemical resistance and can tolerate occasional (not continuous) steam contact.
What About Cost: Is FKM Worth the Premium?
FKM is often the most expensive of the common rubber types. This premium reflects its chemical makeup and manufacturing complexity. But higher cost does not mean universal superiority.
Price Positioning
FKM rubber is a premium product that typically costs significantly more than EPDM. This price difference makes material selection important for budget-conscious projects.
EPDM offers excellent value when the application suits its properties. Paying the FKM premium for a water treatment application wastes money and could actually reduce 씰 수명을 연장합니다..
When to Invest in FKM
FKM justifies its premium cost in these scenarios:
- High-temperature continuous operation above 150C
- Oil and fuel exposure in pumps and fuel systems
- Aggressive chemical environments requiring 70% fluorine grades
- High-pressure applications approaching 3,000 PSI
- Applications where seal failure creates safety or environmental risks
For these conditions, FKM’s performance advantages outweigh the higher material cost. Seal replacement costs and downtime quickly exceed the material price difference.
When EPDM Delivers Better Value
EPDM provides superior value for:
- Water-based applications including potable water systems
- Steam service and boiler applications
- Outdoor installations with UV and ozone exposure
- Cold temperature operation below -30C
- Budget-conscious projects with suitable operating conditions
- High-volume applications where material cost matters
Choosing EPDM where appropriate saves money without sacrificing performance. In fact, using EPDM for water applications actually improves seal life compared to FKM.
Application Decision Matrix: FKM vs EPDM by Industry
Each industry has typical operating conditions that favor one elastomer over the other. Use these recommendations as starting points, then verify against your specific fluid and temperature requirements.
Water Treatment and HVAC
Recommended: EPDM
Water treatment facilities and HVAC systems primarily handle water at various temperatures. EPDM’s water resistance and cost-effectiveness make it the standard choice for these industries.
용도: 원심 펌프용 기계식 씰 물 관련 용도에서는 EPDM O-링이 FKM의 가수분해 우려 없이 신뢰성 있는 씰링을 제공합니다.
화학 처리
권장: FKM (화학물질에 따라 등급 지정)
화학 처리 환경은 일반적으로 FKM의 내화학성이 필요한 강력한 유체를 포함합니다. 특정 화학 노출에 맞춰 FKM 등급을 선택하십시오 – 가장 공격적인 응용 분야에는 GF 등급을 사용합니다.
예외: 오일이나 용제 오염 가능성이 없는 수계 화학 공정은 EPDM을 사용할 수 있습니다.
식품 및 음료
수계 제품 및 세정 공정은 EPDM에 유리합니다. 식품 접촉 용도에 적합한 FDA 준수 EPDM 등급이 제공됩니다.
식품 가공 중 오일 및 지방 노출에는 FKM이 필요합니다. 식물성 오일, 동물성 지방 및 오일 베이스 향료는 EPDM 씰을 팽창시킵니다.
자동차 및 운송
연료 시스템에는 FKM이 필요합니다. 가솔린, 디젤 및 바이오연료 혼합물은 모두 EPDM을 손상시킵니다.
브레이크 시스템은 EPDM만 필요합니다. 현재 자동차 산업의 DOT 브레이크 유체 표준 탄성중합체는 EPDM입니다. 브레이크 유체는 비톤(Viton)과 호환되지 않습니다.
냉각 시스템 냉각수 유형에 따라 다릅니다. 순수 수계 냉각수는 EPDM에 적합합니다. 오일이 오염된 냉각수는 FKM이 필요합니다.
제약
물 및 증기 멸균 공정은 EPDM에 유리합니다. 제자리 증기(SIP) 세정 주기는 FKM 씰을 열화시키는 증기를 사용합니다.
용제 기반 공정에는 FKM이 필요합니다. 제약 제조에 사용되는 유기 용제는 FKM의 내화학성이 필요합니다.
결론
작동 조건을 알면 FKM과 EPDM 중 선택이 간단해집니다. 유체 유형, 온도 범위 및 압력 요구 사항을 확인한 후 본 가이드의 재료 특성과 맞춰보십시오.
적합한 기계식 씰용 탄성중합체선정에 도움이 필요하십니까? 당사 엔지니어링 팀이 귀하의 적용 요구 사항을 검토하고 작동 조건에 최적의 재료를 추천해 드릴 수 있습니다.