What Are Gas Lubricated Mechanical Seals
Gas lubricated mechanical seals, also known as dry gas seals, are advanced sealing solutions that use a thin film of pressurized gas to create a non-contacting seal between rotating and stationary components. Unlike traditional wet seals that rely on liquid lubrication, gas seals utilize inert gases like nitrogen or air to maintain a barrier between the process fluid and the atmosphere.
Design of Gas Lubricated Mechanical Seals
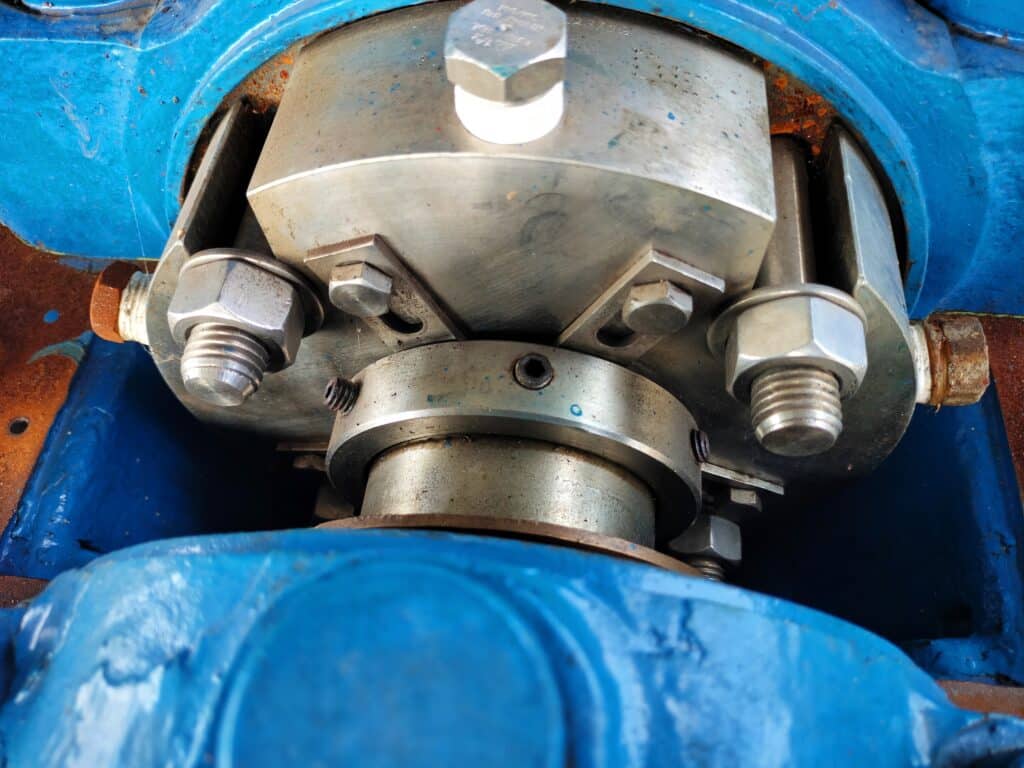
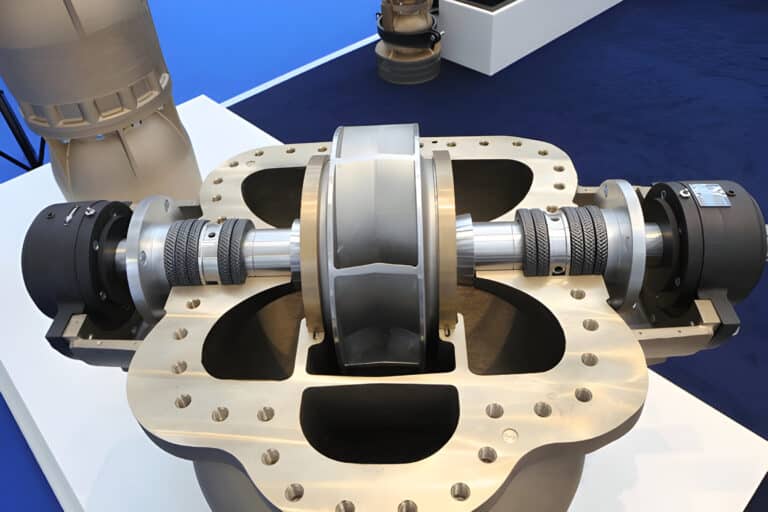
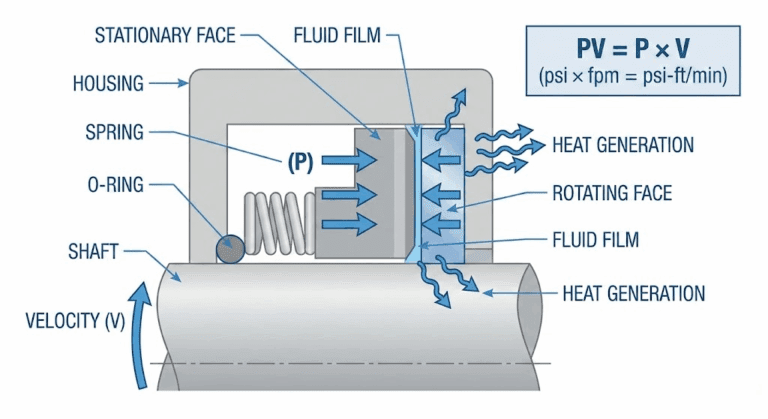
Gas lubricated seals consist of two main components: a rotating primary seal ring and a stationary mating ring. The primary seal ring features spiral grooves etched onto its face, which generate a hydrodynamic lifting force when exposed to the rotating shaft. This lifting force creates a thin gas film between the seal faces, allowing them to operate without physical contact, thereby minimizing friction and wear.
How Gas Lubricated Seals Work
The working principle of gas lubricated seals relies on the hydrodynamic effect generated by the spiral grooves on the primary seal ring face. As the shaft rotates, the grooves pump gas between the seal faces, creating a high-pressure film that separates the rings. The gas film’s thickness is typically in the range of a few microns, depending on factors such as shaft speed, gas viscosity, and seal face geometry.
To maintain a stable gas film, gas seals require a continuous supply of clean, dry gas at a pressure slightly higher than the process fluid. This barrier gas is usually supplied from an external source and is regulated by a control system that adjusts the pressure based on operating conditions.
Advantages of Gas Lubricated Seals
- Reduced friction and wear: The non-contacting nature of gas seals eliminates the friction and wear associated with seal face contact, resulting in extended seal life and reduced maintenance costs.
- Lower power consumption: The absence of liquid lubrication and the minimal frictional losses in gas seals lead to reduced power consumption compared to wet seals.
- Improved process purity: Gas seals prevent the contamination of process fluids by eliminating the need for liquid lubricants, making them ideal for applications that require high product purity.
- Enhanced environmental performance: The use of inert barrier gases and the elimination of liquid leakage make gas seals an environmentally friendly sealing solution, helping industries comply with increasingly stringent emission regulations.
- Wider range of operating conditions: Gas seals can handle a broader range of temperatures, pressures, and shaft speeds compared to liquid-lubricated seals, making them suitable for diverse applications.
Applications of Gas Lubricated Seals
- Oil and gas industry: Gas seals are extensively used in compressors, turbines, and pumps in upstream, midstream, and downstream oil and gas operations. They provide reliable sealing solutions for handling hydrocarbons, natural gas, and other process fluids.
- Chemical processing: The chemical industry relies on gas seals for sealing rotating equipment in the production of a wide range of chemicals, polymers, and petrochemicals. Gas seals offer compatibility with various process fluids and help maintain product purity.
- Power generation: Gas seals are employed in steam turbines, gas turbines, and other rotating machinery in power plants. They ensure efficient and reliable operation while minimizing maintenance requirements.
- Pharmaceutical and food processing: In industries where product contamination is a critical concern, gas seals provide a clean and reliable sealing solution. They prevent the ingress of contaminants and maintain the integrity of the process fluids.
- Refining and petrochemical: Gas seals play a vital role in refining and petrochemical plants, sealing equipment such as compressors, pumps, and mixers. They offer superior performance in handling hydrocarbons, solvents, and other challenging process fluids.