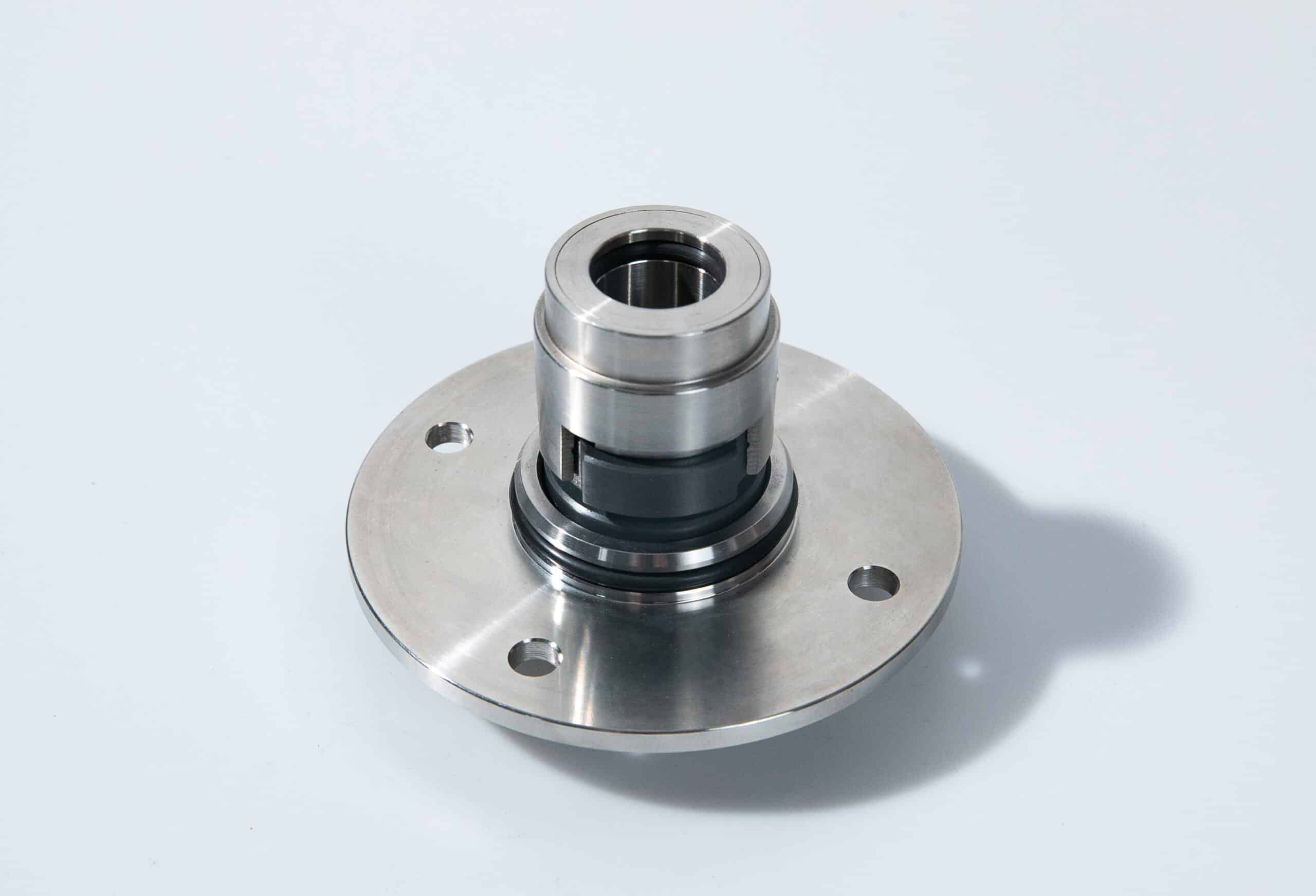
Foot valves are essential components in pumping systems, ensuring efficient operation and protecting equipment from damage. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what foot valves are, how they work, their key benefits, and their applications across various industries, providing you with the knowledge to optimize your pumping system’s performance.

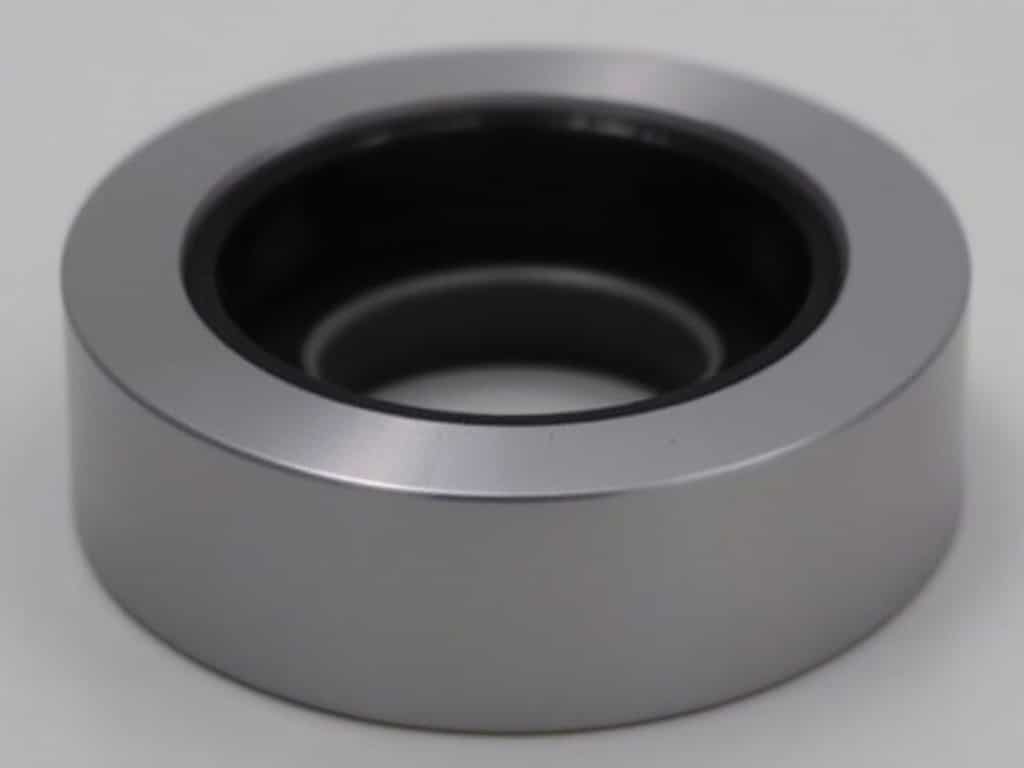
What Is a Foot Valve
A foot valve is a type of check valve installed at the bottom of a pump suction line or pipe. Its primary function is to maintain the prime in the pump by preventing the backflow of liquid when the pump is not in operation.
How Foot Valves Work
Foot valves operate as one-way valves, allowing fluid to flow in only one direction. When the pump is running, the foot valve opens, permitting water or other liquids to enter the suction line. Once the pump stops, the foot valve closes automatically, trapping the fluid in the pipe above the valve. This process ensures that the pump remains primed and ready to start without the need for manual priming.
Parts of Foot Valve
A typical foot valve consists of several key components:
- Screen or Strainer: A screen or strainer is located at the inlet of the foot valve to filter out debris, sand, and other particles that could damage the pump or clog the system.
- Disc/Flapper/Ball: The disc, flapper, or ball is the moving part of the valve that opens and closes to control the flow of fluid. It is typically made of metal or plastic and is designed to create a tight seal when closed.
- Body: The body of the foot valve houses the internal components and provides a connection point for the suction pipe. Foot valve bodies are available in various materials, such as brass, stainless steel, or plastic, depending on the application and fluid compatibility requirements.
- Seat: The seat is the surface against which the disc, flapper, or ball seals when the valve is closed. Proper sealing between the moving part and the seat is crucial for preventing backflow and maintaining the pump’s prime.
Benefits of Using Foot Valves
Incorporating a foot valve in your pumping system offers several advantages:
- Keeping Pumps Primed and Ready to Start: By preventing the backflow of liquid, foot valves ensure that the pump remains primed between operating cycles. This eliminates the need for manual priming and allows the pump to start quickly and efficiently.
- Preventing Pump Damage from Dry Running: A primed pump is less likely to experience dry running, which can cause severe damage to the pump’s internal components, such as seals and bearings. Foot valves help protect your investment in pumping equipment by minimizing the risk of dry running.
- Maintaining Fluid in Pipes to Save Energy: When a foot valve keeps the suction line filled with fluid, the pump does not need to work as hard to lift the liquid during startup. This reduces the energy required to prime the pump and can lead to overall energy savings in your pumping system.
- Filtering Debris to Protect Pump and System: The screen or strainer on the foot valve acts as a first line of defense against debris entering the pump and causing damage or clogging. By filtering out particles, the foot valve helps extend the life of your pumping equipment and reduces maintenance requirements.

Applications of Foot Valve
Foot valves find use in a wide range of water applications, including:
- Wells and boreholes
- Irrigation systems
- Water tanks and reservoirs
- Industrial processes
- Aquaculture and fish farming
- Fountains and water features
- Wastewater treatment plants
FAQs
How Regularly Should I Clean the Strainer?
The frequency of cleaning the foot valve strainer depends on the quality of the water being pumped and the amount of debris present. As a general rule, inspect the strainer every few months and clean it when necessary. If you notice a decrease in pump performance or flow rate, it may be a sign that the strainer needs cleaning.
Is a Foot Valve a Check Valve?
Yes, a foot valve is a type of check valve specifically designed for use at the bottom of a pump suction line. Like other check valves, it allows flow in only one direction and prevents backflow when the pump is not running.
What Is the Difference between a Foot Valve and a Check Valve?
While both foot valves and check valves serve the purpose of preventing backflow, there are some key differences:
- Location: Foot valves are installed at the bottom of the suction line, typically submerged in the liquid source. Check valves can be installed anywhere along the pipeline to prevent reverse flow.
- Strainer: Foot valves often include a built-in strainer to filter out debris, whereas check valves generally do not have this feature.
- Priming: The primary purpose of a foot valve is to maintain the pump’s prime, while check valves are used more broadly to prevent backflow in various applications.
Where Is a Foot Valve Usually Installed?
Foot valves are typically installed at the bottom of the pump suction line or pipe submerged in the liquid source. This location allows the foot valve to effectively maintain the pump’s prime and prevent backflow when the pump is not in operation.
Can a Pump Work without a Foot Valve?
While it is possible for a pump to operate without a foot valve, using one offers significant benefits. Without a foot valve, the pump may lose its prime between operating cycles, requiring manual priming before each start. This can be time-consuming and may lead to increased wear on the pump due to dry running. In most cases, installing a foot valve is recommended to maintain the pump’s prime, prevent backflow, and protect the pumping equipment.
Conclusion
Foot valves play a crucial role in maintaining the efficiency and longevity of pumping systems. By preventing backflow and keeping pumps primed, foot valves reduce energy consumption, protect equipment from damage, and minimize maintenance requirements. When selecting a foot valve for your application, consider factors such as material compatibility, flow requirements, and debris filtration to ensure optimal performance and reliability.