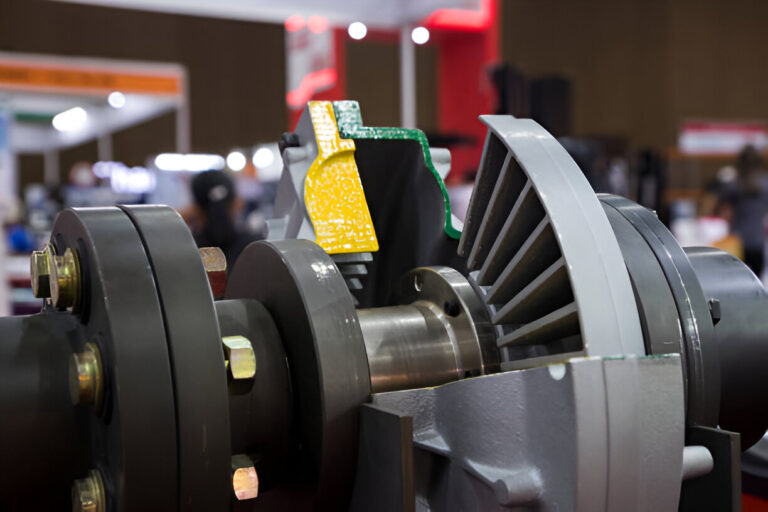
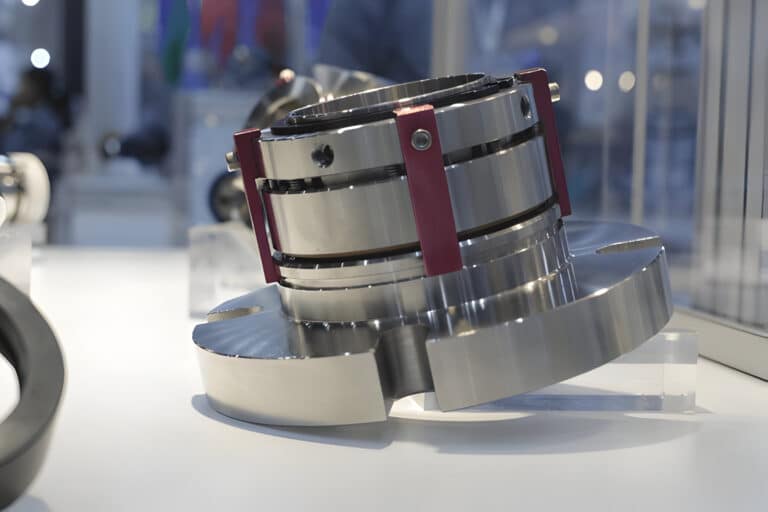
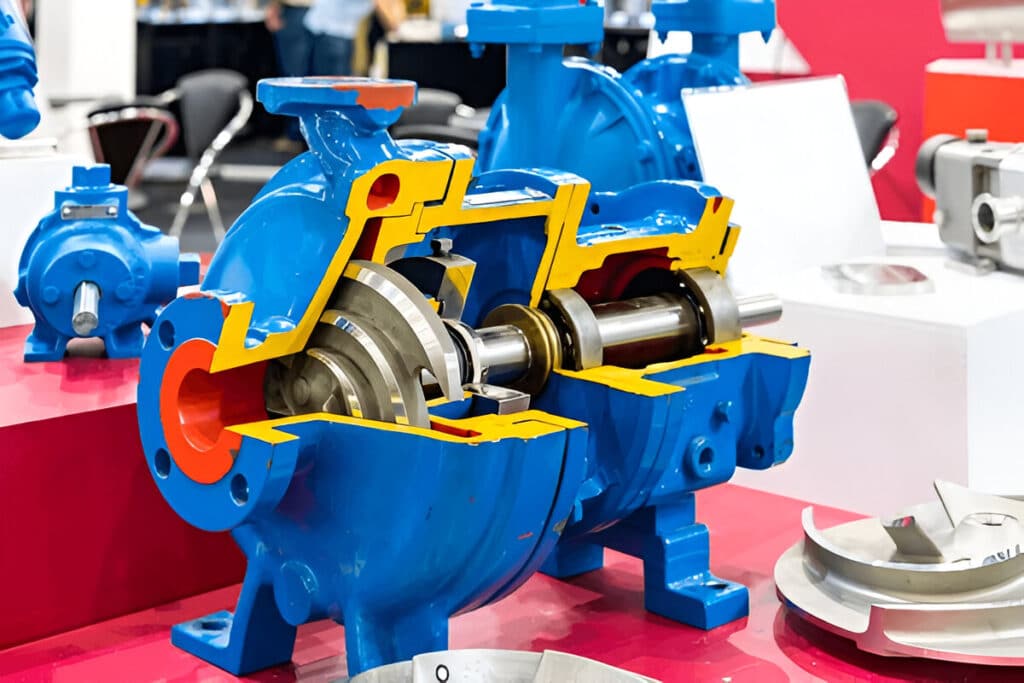
Mechanical seal failure is a frustrating and costly problem that plagues many industrial operations.
From improper installation to contamination to extreme operating conditions, the potential causes are numerous and often difficult to diagnose. Left unchecked, seal failures can lead to unplanned downtime, lost production, and expensive repairs.
In this post, we’ll break down the most common causes of mechanical seal failure and provide actionable tips to help you identify and address issues before they snowball into major problems.

Dry Running
Mechanical seal failure can occur due to several causes, with dry running being one of the most common. Dry running happens when the seal faces operate without proper lubrication from the pumped fluid. This can be caused by:
- Insufficient fluid level in the pump: If the fluid level drops below the minimum required for the pump to operate properly, it can cause the seal to run dry.
- Clogged suction strainer: A clogged strainer can restrict flow to the pump, leading to insufficient fluid reaching the seal faces.
- Closed discharge valve: If the discharge valve is closed while the pump is running, it can cause the fluid to heat up and vaporize, resulting in dry running of the seal.
- Stuck check valve: A stuck check valve can prevent fluid from reaching the seal faces, causing them to run dry.
Improper Installation
Improper installation is another frequent cause of mechanical seal failure. Some common installation issues include:
- Misalignment: Misalignment between the pump and motor shafts can cause excessive vibration and uneven wear on the seal faces, leading to premature failure.
- Incorrect seal size: Installing a seal of the wrong size can result in leakage or accelerated wear.
- Over-tightening fasteners: Applying too much torque when tightening the fasteners can distort the seal faces, causing leakage.
- Damaged seal faces: Seal faces that are scratched, chipped, or otherwise damaged during installation may fail prematurely.
- Excessive shaft play: Too much axial or radial play in the shaft can cause misalignment and uneven loading on the seal faces.
Contamination
Contamination of the pumped fluid or the flush fluid can also lead to mechanical seal failure. Common sources of contamination include:
- Solids in the fluid: Abrasive particles such as sand, rust, or wear debris can get caught between the seal faces, causing scratches and accelerated wear.
- Contaminated flush fluid: If the flush fluid used to cool and lubricate the seal is contaminated with solids or incompatible chemicals, it can damage the seal faces and elastomers.
Vibration
Excessive vibration can cause mechanical seals to fail prematurely. Common sources of vibration include:
- Pump imbalance: An imbalanced impeller or rotor can create vibration that is transmitted to the seal.
- Misalignment: Misalignment between the pump and driver can generate vibration that damages the seal.
- Operating outside the Best Efficiency Point (BEP): Running the pump too far from its BEP can increase vibration levels.
- Worn bearings: Bearings that are worn or damaged can allow excessive shaft movement and vibration.
Chemical Incompatibility
Mechanical seals are constructed from a variety of materials, including metals, ceramics, and elastomers. If these materials are not compatible with the pumped fluid, chemical attack can occur, leading to seal failure. Common compatibility issues include:
- Swelling or softening of elastomers: Exposure to certain chemicals can cause elastomeric seal components (e.g., O-rings) to swell, soften, or degrade, compromising their sealing ability.
- Chemical attack on seal faces: Corrosive chemicals can etch or pit the seal face materials, causing increased leakage and reducing seal life.
Extreme Operating Conditions
Mechanical seals are designed to operate within specific temperature and pressure ranges. When exposed to conditions beyond these limits, seal failure becomes significantly more likely:
- High temperatures: Operating a mechanical seal at temperatures beyond its rated limits will degrade the seal faces, elastomers, and other components.
- High pressures: Exposing a seal to pressures above its specifications puts excessive stress on the seal faces, springs, and secondary seals.
- Pressure spikes: Sudden spikes in system pressure, even if short in duration, impart shock loads that can chip, crack or completely fracture seal faces.
Improper Seal Flush Plan
An ineffective seal flush plan will not adequately cool and clean the mechanical seal, resulting in heat damage and seal face contamination. Common flush plan issues include:
- Inadequate cooling: If the flush fluid fails to remove enough heat from the seal chamber, the seal will operate at elevated temperatures causing degradation of seal components and fluids. Overheating leads to coking of carbonaceous fluids and crystallization of some chemicals which rapidly abrades seal faces.
- Contamination: A flush plan must prevent process fluid and environmental contaminants from entering the seal chamber. Abrasive particles will embed in the soft seal face and scratch the hard face. Solids buildup on seal components restricts movement and causes hang-up.
- Air entrapment: Air bubbles entering the flush port migrate to the seal faces where they cause pitting, chipping and thermal damage. Dissolved air in the flush fluid will come out of solution in low pressure regions near the atmospheric side of the seal faces.
Shaft Movement and Runout
Mechanical seals rely on precise alignment and concentricity between the shaft and seal faces. Excessive shaft movement or runout can cause seal failure through several mechanisms:
- Worn bearings: As bearings wear, increased clearance allows the shaft to orbit within the bearing envelope. This radial shaft movement causes cyclical axial displacement of the seal components, resulting in vibration, fatigue and seal face damage. Severe bearing wear can allow shaft-to-seal contact.
- Bent shaft: A shaft bend will produce an oscillating axial displacement of the seal components as the shaft rotates. Like a worn bearing, this prevents the seal faces from maintaining proper contact. Misalignment from a bent shaft concentrates loading on one spot of the seal face, leading to premature wear.
Cavitation
Cavitation occurs when localized fluid pressure drops below the vapor pressure, forming vapor cavities or bubbles. As these bubbles collapse near the seal faces, they can cause significant damage:
- Erosion of seal faces: The implosion of cavitation bubbles generates high-velocity micro-jets and shock waves that progressively erode the seal face material. The resulting pits and surface irregularities disrupt the seal face flatness and fluid film, causing leakage.
- Vibration: Cavitation within the seal chamber induces intense high-frequency vibrations. These vibrations can cause seal component fatigue, secondary seal damage, and increased wear due to disrupted lubricating films between faces.