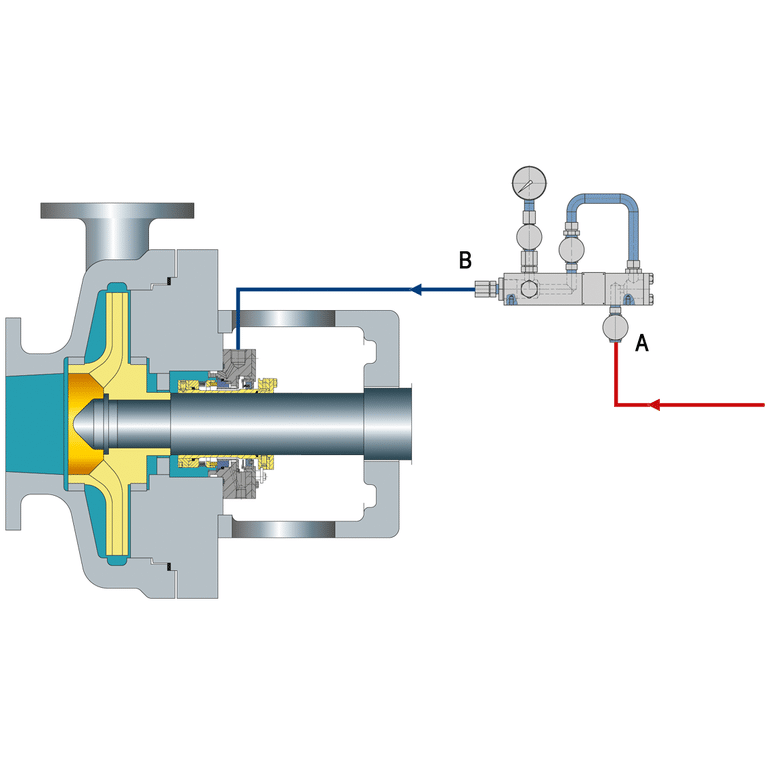
What is API Plan 52
API Plan 52 is a piping arrangement used to provide clean, cool flush fluid to the mechanical seal of a pump. It is part of the American Petroleum Institute’s (API) standard 682, which defines various piping plans for mechanical seals in centrifugal pumps used in the petroleum, natural gas, and chemical industries.
API Plan 52 is considered a reliable and effective method for sealing rotating equipment, as it provides continuous lubrication and containment of the process fluid. However, it does require additional components and maintenance compared to simpler seal arrangements, making it more suitable for critical applications or when handling hazardous fluids.
How Does API Plan 52 Work
API Plan 52 involves an external reservoir that holds a buffer fluid, usually a clean, compatible liquid. This reservoir is connected to the seal chamber of the pump through piping and a cooler.
The cooling water or another cooling medium flows through the tubes of the cooler, while the buffer fluid from the reservoir flows through the shell side of the cooler. This allows the buffer fluid to be cooled before entering the seal chamber.
The cooled buffer fluid then enters the seal chamber, where it surrounds the mechanical seal.
The buffer fluid circulates between the seal chamber and the reservoir continuously. As it returns to the reservoir, it carries any heat or contaminants away from the seal.
The reservoir also acts as a collection point for any leakage from the mechanical seal. If the seal leaks, the leaked fluid is captured in the reservoir, preventing it from entering the process stream or the environment.
Additionally, the reservoir provides a means of monitoring the condition of the mechanical seal. Changes in the level or appearance of the buffer fluid can indicate seal wear or failure, allowing for proactive maintenance.
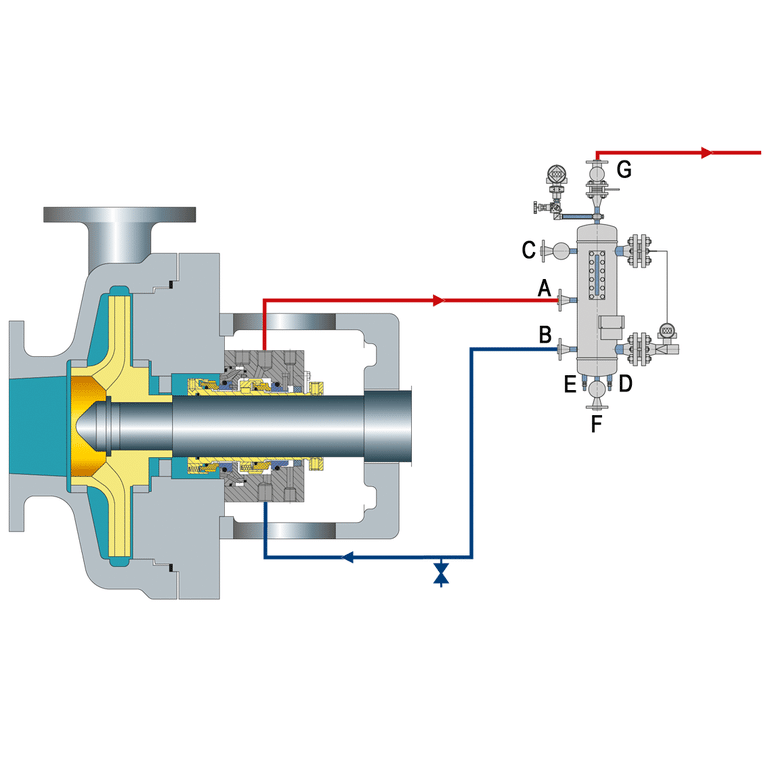
Design of API Plan 52
- buffer fluid Reservoir: Holds buffer fluid for seal lubrication and heat dissipation, equipped with a level gauge, drain, and vent.
- Pressure Intensifier: Uses devices like piston or bladder accumulators to keep buffer fluid pressure above that of the pumped fluid, preventing contamination.
- Circulation System: Continuously circulates buffer fluid between the reservoir and seal chamber to manage temperature and remove heat.
- Cooling: May include a cooler, such as a heat exchanger or finned tube, in the loop to dissipate excess heat.
- Pressure Regulation: Features a pressure regulator to maintain a constant pressure differential, ensuring seal lubrication and preventing fluid mixing.
- Filtration: Incorporates a filter in the circulation system to remove contaminants and extend seal life.
- Seal Chamber: Designed to accommodate the mechanical seal, with ports for circulation and a drain for maintenance.
- Instrumentation: Includes pressure gauges, level switches, and temperature sensors for monitoring buffer fluid conditions.
- Materials of Construction: Made from materials like stainless steel or engineered plastics for compatibility and corrosion resistance.
Advantages of API Plan 52
- Provides a clean, cool environment: For the mechanical seal, reducing wear and increasing seal life.
- Prevents process fluid from entering the seal chamber: Reducing the risk of seal failure due to contamination or high temperature.
- Can be used with a wide range of process fluids and operating conditions: Ensuring versatility and adaptability.
- Relatively simple and cost-effective: Compared to other API piping plans, offering economic advantages.
Disadvantages of API Plan 52
- Requires a Reliable External Flush Fluid Source: This may not always be available, posing operational challenges.
- Dilution of Process Fluid: The flush fluid can dilute the process fluid, which may be undesirable in some applications.
- Treatment or Disposal Costs: The discharged flush fluid and process fluid mixture may require treatment or disposal, adding to operating costs.
- Unsuitable for High Solids or Abrasive Fluids: Not suitable for processes with high solids content or highly abrasive fluids, as these can clog the flush fluid injection ports or damage the seal faces.
Applications
- Oil and gas industry
- Chemical processing
- Refineries
- Power generation
- Pulp and paper mills
- Mining and mineral processing
- General industrial applications