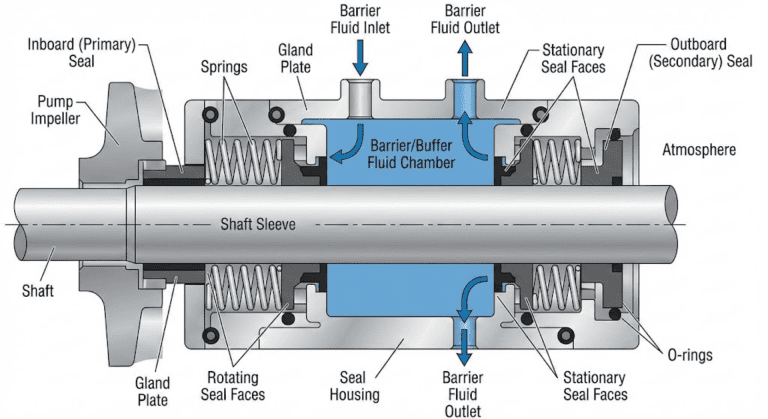
A double mechanical seal cooling system uses two seals with a barrier fluid in between to prevent leakage in high-pressure or hazardous environments. The cooling system regulates the temperature of the barrier fluid using a heat exchanger, pump, or thermosiphon to protect seal integrity and maintain system reliability.
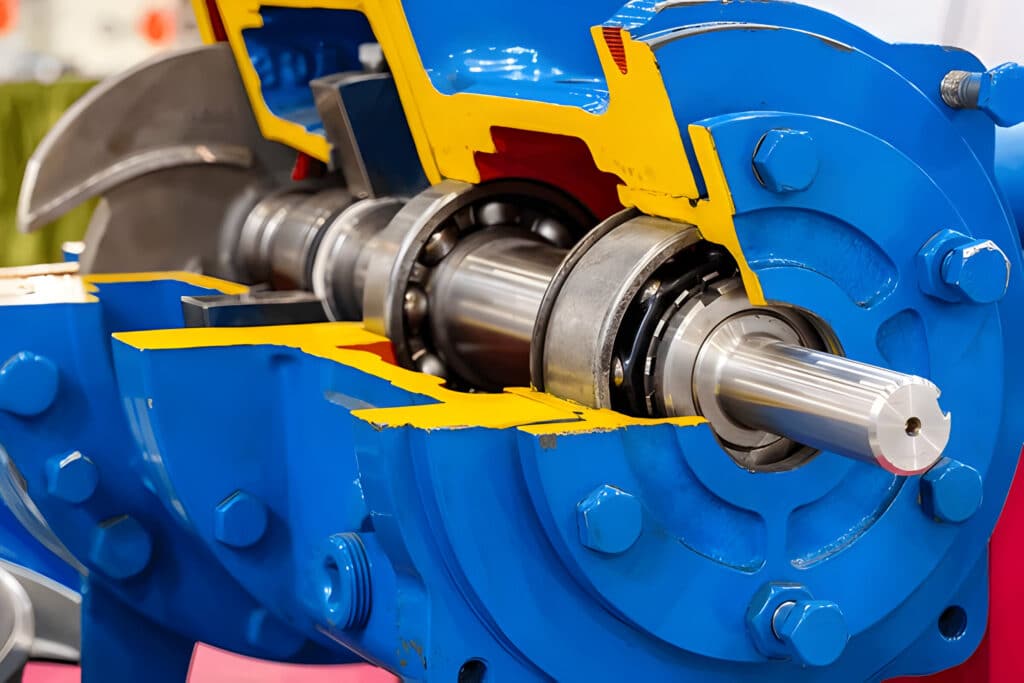

Types of Double Mechanical Seal Cooling Systems
Open Loop Systems
Open loop systems supply pressurized barrier fluid continuously to the seal chamber. After the fluid circulates through the seal, it expands and gets collected in an unpressurized reservoir or discharged from the system entirely.
This design requires a constant supply of fresh fluid. The used fluid either gets recycled back to the process or disposed of.
Closed Loop Systems
Closed loop systems recirculate a fixed volume of barrier or buffer fluid within a dedicated circuit. This circuit includes the seal chamber, connecting piping, heat exchanger, and reservoir.
The system maintains fluid pressure through external gas sources acting on reservoirs or through accumulators. This design is more economical for expensive barrier fluids since it minimizes fluid consumption.
Circulation Methods
Thermosiphon Effect
The thermosiphon effect provides passive circulation without external pumps. This natural convection process occurs when barrier fluid near hot seal components heats up, becomes less dense, and rises through piping to reach a heat exchanger or reservoir positioned above the seal.
In the cooler area, the fluid releases heat, increases in density, and flows back down to the seal chamber. This creates a continuous circulation loop driven entirely by temperature differences.
Forced Circulation
- Pumping Rings (Internal Circulating Devices): Pumping rings are components built into the mechanical seal cartridge that rotate with the pump shaft. These miniature pumps create flow of barrier fluid through the seal chamber and any connected external loops.
- External Pumps: External pumps draw barrier fluid from reservoirs and circulate it through heat exchangers and filters before supplying it to the seals. These pumps provide consistent flow rates regardless of temperature differences.
API Piping Plans for Double Mechanical Seal Cooling
Buffer Fluid Systems (Unpressurized – API Arrangement 2 Type Seals)
Buffer fluid systems work with API Arrangement 2 dual seals. The space between inboard and outboard seals contains buffer fluid maintained at pressure lower than the process pressure.
The buffer fluid lubricates outboard seal faces, removes heat from both seals, and contains any leakage from the inboard seal. This arrangement prevents process fluid from reaching the atmosphere.
- API Plan 52: Uses an external tank to hold and cool the unpressurized buffer fluid.
Barrier Fluid Systems (Pressurized – API Arrangement 3 Type Seals)
Barrier fluid systems are used with API Arrangement 3 dual seals. The barrier fluid pressure in the inter-seal cavity exceeds the process pressure, creating a positive pressure differential.
This pressure difference ensures that any inboard seal leakage consists of clean barrier fluid entering the process. Any outboard seal leakage releases only small amounts of clean barrier fluid to atmosphere.
- API Plan 53A: Pressurized Barrier Fluid from Reservoir.
- API Plan 53B: Pressurized Barrier Fluid via Bladder Accumulator.
- API Plan 53C: Pressurized Barrier Fluid via Piston Accumulator.
- API Plan 54: External Pressurized Barrier Fluid System.
- API Plan 55: External Unpressurized Buffer Fluid System.
Relevant Process Side Plans
- API Plan 21: Sends cooled process fluid from pump discharge to the seal.
- API Plan 23: Uses a pumping ring in a closed loop to move cooled fluid.
- API Plan 32: Delivers clean external fluid to flush the seal.
Atmospheric Side Plans (Quench)
- API Plan 62: Sends a small stream of fluid or gas to the seal’s outside edge to prevent contamination or icing.
Components of Double Mechanical Seal Cooling Systems
- Heat Exchangers (Seal Coolers): Heat exchangers remove thermal energy from barrier or buffer fluids. These units typically use water, air, or other cooling media to maintain fluid temperatures within acceptable ranges for seal operation.
- Reservoirs: Reservoirs store barrier or buffer fluids and provide expansion volume for thermal growth. They often include level indicators, temperature sensors, and connections for fluid makeup or drainage.
- Pumping Rings: Pumping rings are internal circulation devices that rotate with equipment shafts. They generate flow through seal chambers and external cooling systems without requiring separate pumps.
- Accumulators: Accumulators maintain consistent pressure in barrier fluid systems. Bladder and piston types store pressurized fluid and compensate for volume changes due to temperature fluctuations or minor leakage.
- Cyclone Separators: Cyclone separators remove entrained gas bubbles from barrier or buffer fluids. Gas removal prevents seal face separation and maintains proper lubrication film thickness.
- Instrumentation and Control: Control systems monitor temperature, pressure, flow rate, and fluid levels. They provide alarms for abnormal conditions and can automatically adjust system parameters to maintain optimal seal operating conditions.