Do you want to keep your pump in top condition? Proper maintenance is essential for ensuring your pump operates efficiently and lasts longer.
In this blog post, we’ll provide you with simple tips on how to maintain your pump. By following these guidelines, you can prevent common issues and extend the life of your pumping equipment.

Types of Pump Maintenance
Preventive (Proactive) Maintenance
Preventive maintenance is a proactive approach that involves regular inspections, lubrication, and minor adjustments to prevent pump failures. This type of maintenance helps maintain optimal performance, reduce energy bills, and extend the life of the pump.
Predictive Maintenance & Condition Monitoring
Predictive maintenance utilizes monitoring devices to track pump performance and detect potential issues before they lead to failure. By monitoring vibration levels, temperature, and other key parameters, maintenance personnel can make informed decisions about when to perform repairs or replacements.
Corrective (Reactive) Maintenance
Corrective maintenance is performed when a pump has already failed or is showing signs of damage. This type of maintenance is often more costly and time-consuming than preventive or predictive maintenance, as it may involve significant repairs or replacements.
To minimize the need for corrective maintenance, it is essential to implement a comprehensive maintenance plan that includes regular inspections, lubrication, and condition monitoring. By catching and addressing issues early, pump owners can avoid costly downtime and extend the life of their equipment.
Daily Checklist
- Inspect all safety devices, guards, and emergency stops to ensure proper functioning.
- Check fluid levels, including oil, coolant, and hydraulic fluids, and top up if necessary.
- Examine belts, hoses, and other visible components for signs of wear, damage, or leaks.
- Clean and lubricate moving parts as specified in the manufacturer’s guidelines.
- Verify that all gauges, indicators, and warning lights are working correctly.
- Test run the equipment to identify any unusual noises, vibrations, or performance issues.
- Ensure that the work area around the equipment is clean, organized, and free of hazards.
Monthly & Quarterly Checklist
- Inspect and clean all air filters, replacing them if necessary. Dirty filters can lead to reduced efficiency and increased energy consumption.
- Check and adjust belts for proper tension. Loose or worn belts can cause poor performance and damage to equipment.
- Lubricate moving parts, such as bearings and hinges, to reduce friction and prevent premature wear. Use the appropriate lubricant for each component.
- Test and calibrate sensors and controls to ensure accurate readings and proper system operation. This includes temperature, pressure, and flow sensors.
- Examine electrical connections and wiring for signs of damage, loose connections, or corrosion. Tighten or replace as needed to maintain safe and reliable operation.
- Verify the proper functioning of safety devices, such as emergency stops, interlocks, and pressure relief valves. These devices are crucial for preventing accidents and injuries.
- Conduct visual inspections of equipment exteriors and interiors for signs of wear, damage, or leaks. Address any issues promptly to prevent further deterioration.
- Clean and organize the work area around the equipment to maintain a safe and efficient environment. Remove any debris, tools, or materials that could cause tripping hazards or obstruct access to the equipment.
Annual Checklist
- Inspect and calibrate all sensors, gauges, and monitoring devices to ensure accurate readings.
- Test and replace batteries in backup power systems, such as uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) and emergency lighting.
- Clean and lubricate all moving parts, including bearings, gears, and hinges, to prevent wear and tear.
- Tighten and adjust all belts, chains, and couplings to maintain proper tension and alignment.
- Inspect and replace filters in HVAC systems, compressed air systems, and hydraulic systems to maintain efficiency and prevent contamination.
- Test and recertify all safety devices, such as fire alarms, sprinkler systems, and emergency shut-off valves, to ensure proper functioning.
- Conduct thermographic inspections of electrical systems to identify potential hot spots and prevent electrical fires.
- Perform oil analysis on critical equipment to detect wear particles and contaminants that could indicate impending failure.
- Update and back up all software and firmware to the latest versions to ensure compatibility and security.
- Review and update all preventive maintenance schedules and procedures to incorporate any changes in equipment or operating conditions.
Optimizing Pump Reliability & Performance
Operating Near Best Efficiency Point (BEP)
Operating pumps near their BEP ensures optimal performance and longevity. Deviating significantly from the BEP can lead to increased vibration, reduced efficiency, and premature wear.
Maintaining Correct Alignment
Proper alignment between the pump and driver is crucial for minimizing vibration and extending equipment life. Regularly check and correct any misalignment using precision tools and techniques.
Selecting Suitable Mechanical Seals and Flush Plans
Choose mechanical seals and flush plans that are compatible with the pumped fluid and operating conditions. Ensure proper installation and maintenance of seals to prevent leaks and failures.
Controlling Process Variables
Monitor and control process variables such as NPSH, gas entrainment, and solids concentration. Inadequate NPSH, excessive gas, or abrasive solids can severely damage pump internals and degrade performance.
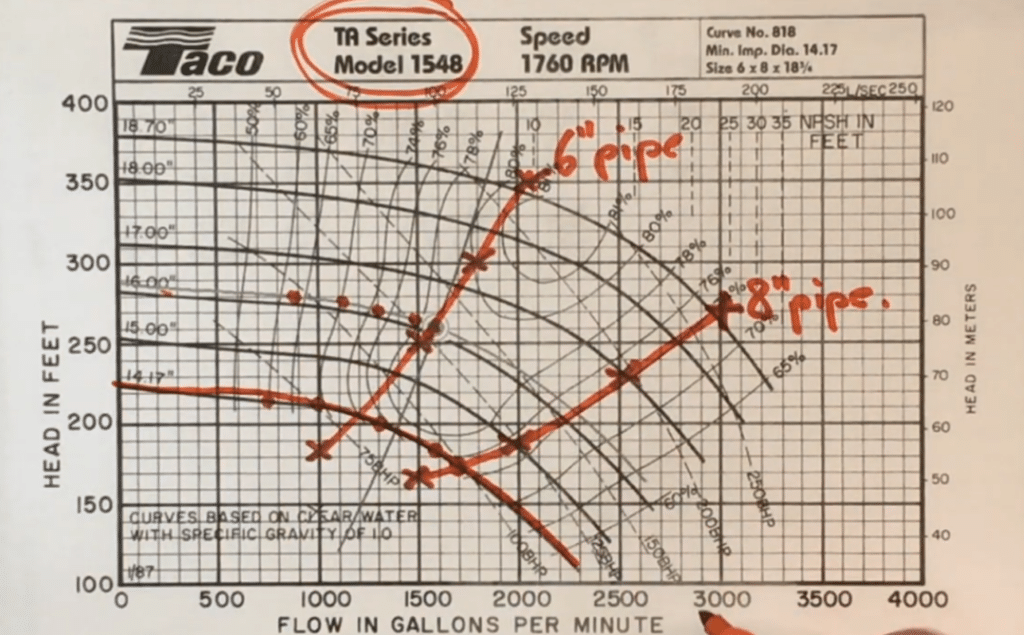
Monitoring Pump Curves
Regularly assess pump performance curves to detect internal wear and recirculation. Comparing current curves to the original manufacturer’s curve helps identify efficiency losses and potential maintenance requirements.
FAQs
How often should I perform pump maintenance?
Perform routine maintenance at least once a year or as recommended by the manufacturer. More frequent maintenance may be necessary for pumps under heavy use or in harsh environments.
How long does a typical pump last?
Pump lifespan varies by type, application, and maintenance. With proper maintenance, pumps can last 10-15 years or more.
In Conclusion
Proper pump maintenance is essential for optimal performance and longevity. By following this guide, you can ensure your pumps remain in top condition and avoid costly repairs or downtime.
Implement these maintenance practices today and enjoy the benefits of a well-maintained pumping system. Visit our website for more expert tips and resources on pump maintenance and efficiency.