What is pump motor alignment and why is it crucial for your equipment’s performance and longevity?
Pump motor alignment is the process of ensuring that the pump and motor shafts are correctly aligned. Proper alignment is essential for reducing vibration, minimizing wear and tear, and optimizing energy efficiency.
In this blog post, we’ll dive into the fundamentals of pump motor alignment and provide you with the knowledge to keep your equipment running smoothly and efficiently.
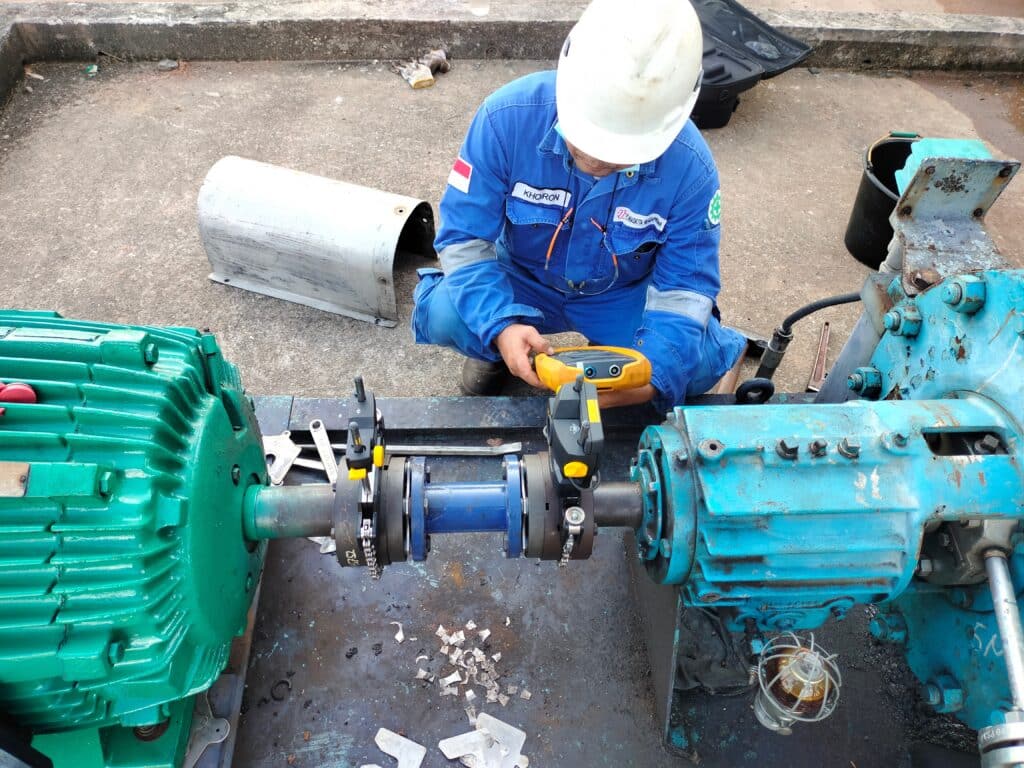

What is Pump Motor Alignment
Pump motor alignment refers to the precise positioning of the pump shaft and motor shaft to ensure they are correctly aligned.
Misalignment can occur in two forms: angular misalignment, where the shafts are at an angle to each other, and parallel misalignment, where the shafts are parallel but not in line.
Misalignment can lead to excessive vibrations, premature wear of pump components, and reduced energy efficiency. Even small degrees of misalignment can cause significant issues over time, resulting in costly repairs and downtime.
How to Align Shafts: Step by Step
Step 1: Preparation
Before beginning the alignment process, ensure that the pump and motor are disconnected from power sources and the coupling is removed. Clean the shaft ends and flanges to remove any dirt or debris.
Gather the necessary tools, such as dial indicators, feeler gauges, and straightedges.
Step 2: Check for Misalignment
Place the straightedge across the coupling halves to check for parallel misalignment. Use feeler gauges to measure any gaps between the straightedge and the coupling halves.
To check for angular misalignment, place the dial indicator on one shaft and rotate both shafts simultaneously. Note any deviations in the readings.
Step 3: Perform Rough Alignment
Adjust the motor position using shims or jack bolts until the straightedge rests evenly on both coupling halves, indicating that the shafts are roughly aligned.
Ensure that the shafts are not under excessive strain during this process.
Step 4: Fine-Tune Alignment
Attach dial indicators to both shafts and take readings in the vertical and horizontal planes. Adjust the motor position until the dial indicator readings are within the acceptable tolerance range specified by the manufacturer.
Rotate the shafts to various positions and recheck the alignment to ensure accuracy.
Step 5: Verify and Document
Once the alignment is complete, reinstall the coupling and tighten the flange bolts. Rotate the shafts by hand to ensure smooth rotation without binding.
Document the final alignment readings and keep them for future reference during maintenance or troubleshooting.
Tips for Pump Alignment
- For more precise alignment, consider using laser alignment tools. These tools provide real-time feedback and can account for factors such as thermal growth and dynamic movement.
- Consider both horizontal and vertical planes when aligning pump shafts. Misalignment can occur in either plane, leading to excessive vibrations, premature wear, and reduced efficiency.
- Account for thermal growth and movement during alignment. As equipment operates, thermal expansion can cause changes in shaft positions, affecting alignment. Consider these factors when setting alignment tolerances.
- Address alignment issues promptly. If excessive vibrations or other signs of misalignment are detected, take corrective action immediately. Delaying repairs can lead to accelerated wear, reduced efficiency, and potential equipment failure.
Pump Alignment Methods
Straight Edge and Feeler Gauge Method
The straight edge and feeler gauge method is a simple and cost-effective way to perform preliminary alignment. Place a straight edge across the coupling halves and use a feeler gauge to measure any gaps, indicating misalignment.
This method can help identify significant misalignment issues but lacks the precision of more advanced techniques.
Dial Indicator Method
Dial indicators provide a more accurate method of measuring shaft alignment. Attach dial indicators to the pump and motor shafts and take readings while rotating the shafts.
This method allows for the detection and correction of both angular and parallel misalignment. However, it requires manual calculations and adjustments.
Laser Alignment Systems
Laser alignment systems are the most accurate and efficient tools for pump shaft alignment. These systems use laser beams to measure alignment offsets and provide real-time feedback during adjustments.
Laser alignment tools can quickly identify and correct misalignment issues, reducing downtime and ensuring optimal pump performance. Many systems also offer built-in alignment calculators and documentation capabilities.
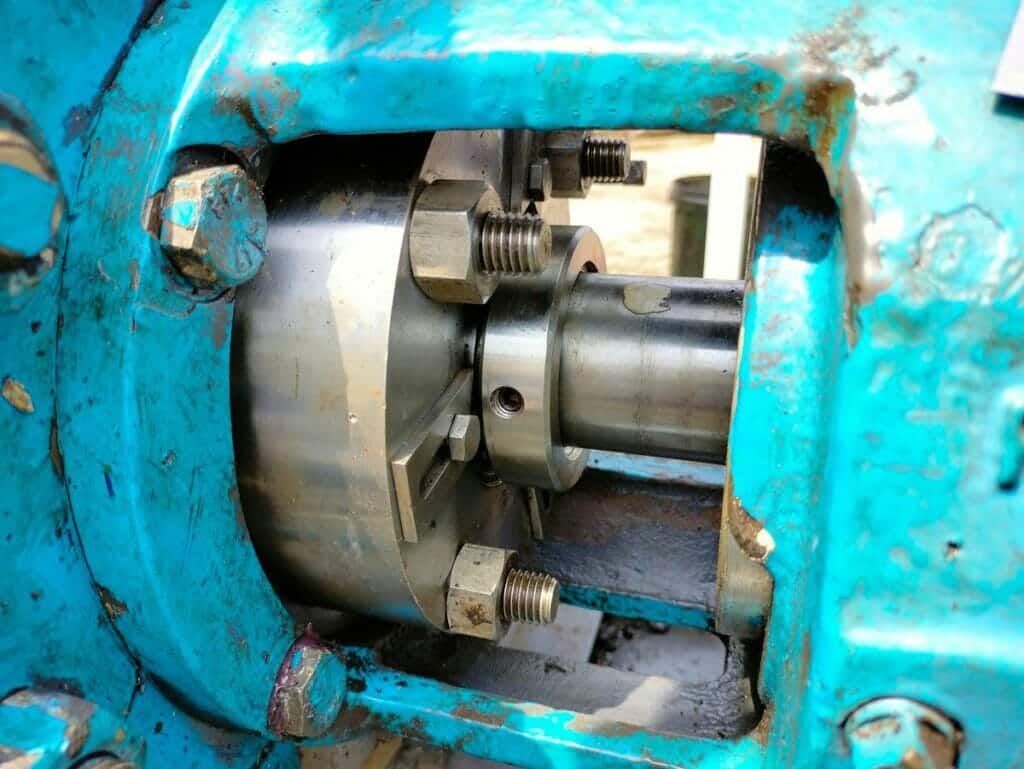

Troubleshooting Common Alignment Issues
Soft Foot
Soft foot is a condition where one or more of the machine feet do not make proper contact with the base plate, causing misalignment. This can be caused by uneven or damaged base plates, loose or damaged foundation bolts, or improper shimming.
To detect soft foot, use a feeler gauge to check for gaps between the machine feet and the base plate. Correct soft foot by adjusting shims, tightening or replacing foundation bolts, and ensuring base plates are level and in good condition.
Coupling Wear and Failure
Coupling wear and failure can be caused by misalignment, excessive vibration, or improper coupling selection. Signs of coupling wear include excessive noise, vibration, and visible damage such as cracks or deformation.
To prevent coupling wear and failure, ensure proper alignment of pump and motor shafts using laser alignment tools or dial indicators. Select couplings appropriate for the application and maintain them according to manufacturer recommendations.
Vibration and Noise
Excessive vibration and noise can indicate misalignment issues in pump and motor shafts. Angular and parallel misalignment can cause increased vibration levels, leading to premature wear and failure of pump components.
Identify misalignment-related problems by monitoring vibration levels using vibration analysis tools and comparing them to acceptable standards. Perform regular alignment checks and corrections using laser alignment systems or other accurate methods.
Bearing and Seal Failure
Misalignment can cause excessive loads on bearings and seals, leading to premature wear and failure. This can result in increased maintenance costs and unplanned downtime.
To prevent bearing and seal failure due to misalignment, ensure accurate alignment of pump and motor shafts during installation and perform regular alignment checks. Use appropriate alignment tools and methods, such as laser alignment systems or dial indicators, and follow manufacturer recommendations for installation and maintenance of bearings and seals.
Benefits of Precision Alignment
- Increased energy efficiency and cost savings
- Reduced wear and tear on equipment components
- Extended machine life and reduced downtime
- Improved safety and reliability
- Compliance with equipment manufacturer specifications and industry standards
- Noise and vibration reduction
FAQs
How often should pump motor alignment be checked?
Alignment should be checked during installation, after maintenance, and periodically (e.g., annually) as part of a preventive maintenance program.
What are the acceptable tolerances for alignment?
Acceptable tolerances depend on factors such as speed, coupling type, and equipment specifications. Generally, angular misalignment should be within 0.002 in/in, and parallel misalignment within 0.002 in.
In conclusion
Proper pump motor alignment is crucial for optimal performance, reduced vibration, and extended equipment life. Regularly checking and correcting alignment issues can prevent costly downtime and repairs.
For expert assistance with pump motor alignment, contact our experienced team today and ensure your system runs smoothly.