Have you ever wondered about the safety measures in industrial fluid systems? Double Block and Bleed (DBB) valves are crucial components in these setups.
DBB valves are specialized devices that provide two layers of isolation and a bleed function. They enhance safety and reliability in piping systems.
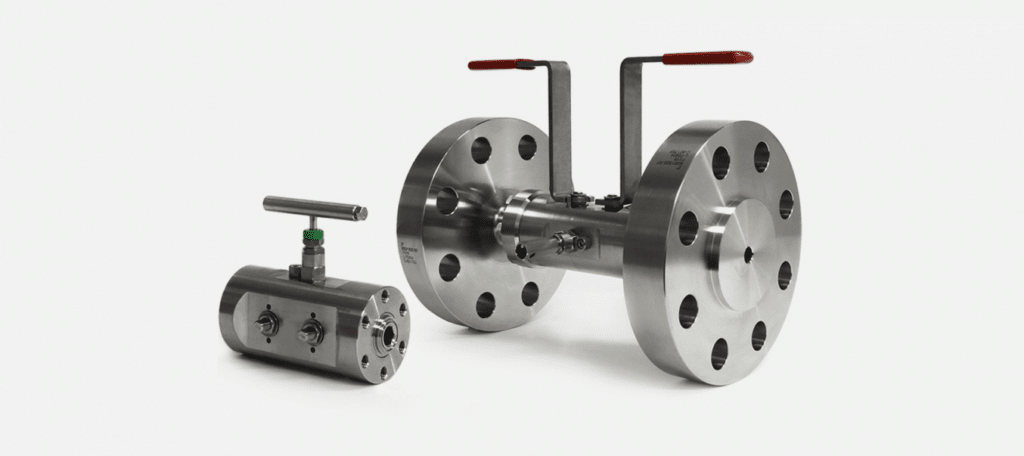
What are Double Block and Bleed Valves
Double Block and Bleed (DBB) valves incorporate two block valves and a bleed valve in a single unit. The block valves provide dual isolation points, sealing against pressure from both upstream and downstream directions.
The bleed valve, positioned between the block valves, allows for venting or draining of the cavity. This design ensures a higher level of isolation compared to single valves.
When closed, the upstream block valve stops fluid flow. The downstream block valve acts as a secondary barrier. The bleed valve then releases any trapped pressure or fluid in the cavity.
Components of DBB Valves
- Valve Body: The valve body is the main housing of a Double Block and Bleed (DBB) valve. It contains all the internal components and provides structural integrity.
- Block Valves: DBB valves typically incorporate two block valves. These are often ball valves or gate valves, designed to seal against pressure from both upstream and downstream directions.
- Bleed Valve: Between the two block valves lies the bleed valve. This smaller valve allows for the release of any trapped fluid or pressure in the cavity between the block valves.
- Seats and Seals: The block valves utilize seats and seals to ensure tight shutoff.
- Actuators: Many DBB valves feature actuators for remote operation. These can be manual, pneumatic, hydraulic, or electric.
Advantages of DBB Valves
- Enhanced safety due to fewer leak points
- Compact design saves space and weight
- Simplifies installation and maintenance
- Enables quick evacuation of trapped pressure in emergencies
- Reduces waste and disposal costs
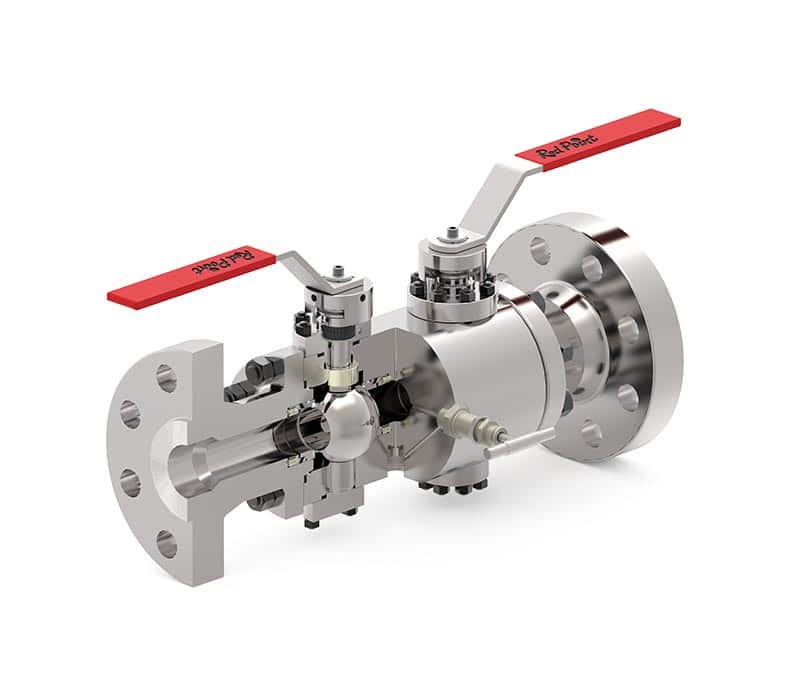

Types of DBB Valves
Gate Valve DBB
Gate valve DBBs are widely used in the oil and gas industry. They offer excellent sealing capabilities against pressure from both directions.
These valves consist of two gate valves and a bleed valve in between. The gate valves act as the primary isolation points.
Ball Valve DBB
Ball valve DBBs are popular in chemical plants and refineries. They provide a tight shutoff and are suitable for high-pressure applications.
These valves feature two ball valves with a bleed valve in the center. The ball valves rotate to control fluid flow.
Plug Valve DBB
Plug valve DBBs are common in the pharmaceutical industry. They offer reliable isolation and are easy to maintain.
These valves incorporate two plug valves and a bleed valve. The plug valves use a tapered or cylindrical plug to control flow.
Needle Valve DBB
Needle valve DBBs are used in instrumentation and small-bore applications. They provide precise flow control and tight shutoff.
These valves consist of two needle valves and a bleed valve. The needle valves use a tapered needle to regulate flow.
Butterfly Valve DBB
Butterfly valve DBBs are suitable for large diameter pipelines. They offer a compact design and low-pressure drop.
These valves feature two butterfly valves with a bleed valve between them. The butterfly valves use a rotating disc to control flow.
Piston Valve DBB
Piston valve DBBs are used in high-pressure applications. They provide excellent sealing and are suitable for corrosive fluids.
These valves incorporate two piston valves and a bleed valve. The piston valves use a moving piston to control flow.
Monoblock DBB
Monoblock DBBs offer a compact solution for space-constrained applications. They combine all components into a single unit.
These valves integrate two block valves and a bleed valve within a single body. This design reduces installation time and potential leak points.
Trunnion-Mounted Ball Valve DBB
Trunnion-mounted ball valve DBBs are used in high-pressure gas applications. They provide excellent sealing and low operating torque.
These valves feature two trunnion-mounted ball valves and a bleed valve. The ball valves are supported on both sides for stability.
Cryogenic DBB
Cryogenic DBBs are designed for extremely low-temperature applications. They maintain their sealing capabilities in harsh conditions.
These valves use specialized materials and designs to withstand cryogenic temperatures. They are commonly used in LNG facilities.
Self-Relieving DBB
Self-relieving DBBs offer additional safety features. They automatically relieve pressure buildup in the valve cavity.
These valves incorporate a self-relieving mechanism in the seats. This prevents over-pressurization between the two block valves.
Factors to Consider When Selecting the Right DBB Valve
Process Fluid Properties
Corrosive fluids require materials with high chemical resistance, while abrasive fluids necessitate hardened valve components.
Temperature and Pressure Ranges
DBB valves must withstand the operating conditions of the system. High-temperature applications may require special alloys, while high-pressure systems demand robust valve designs with appropriate pressure ratings.
Material Compatibility
The valve body, seats, and seals must be compatible with the process fluid to prevent corrosion, erosion, or degradation. Stainless steel and specialized alloys are common choices for chemical and petrochemical applications.
End Connection Types and Sizes
The valve’s end connections must match the piping system. Common types include flanged, welded, and threaded connections.
In Conclusion
Double block and bleed valves are crucial for ensuring safety and efficiency in fluid systems. They provide robust isolation and leak prevention, making them indispensable in various industries.
For more information on implementing double block and bleed valves, consult with a qualified engineer or valve specialist today.




