The American Petroleum Institute (API) publishes standards that govern the design and operation of equipment used in the oil and gas industry. Two such standards, API 610 and API 682, are particularly noteworthy for their impact on centrifugal pumps and mechanical seals respectively.
While both standards aim to enhance reliability, efficiency, and safety in the petroleum industry, they differ in their specific areas of focus and technical requirements. This article will delve into the key distinctions between API 610 and API 682, examining their scope, technical aspects, and interrelationship to provide a comprehensive understanding of these critical industry standards.

What Is API 610
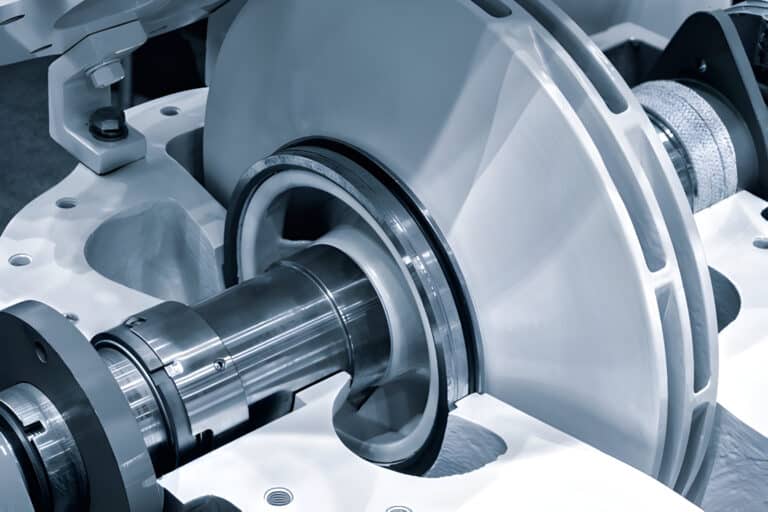
API 610 is an international standard developed by the American Petroleum Institute (API) that specifies the requirements for centrifugal pumps used in the petroleum, petrochemical, and natural gas industries. This standard covers the design, materials, manufacturing, testing, and documentation of centrifugal pumps.
API 610 pumps are typically used for critical applications in refineries, chemical plants, and offshore platforms, where reliability and performance are of utmost importance. These pumps are designed to handle a wide range of fluids, including crude oil, refined products, chemicals, and water.
The standard includes provisions for various pump types, such as overhung pumps, between-bearings pumps, and vertically suspended pumps. It also covers different pump configurations, including single-stage and multistage designs, as well as different impeller types and shaft sealing arrangements.
API 610 sets stringent requirements for materials, manufacturing processes, and quality control to ensure that the pumps can withstand the demanding conditions encountered in the oil and gas industry. The standard also specifies requirements for testing, including hydrostatic, performance, and mechanical run tests, to verify the pump’s integrity and performance before installation.
What Is API 682
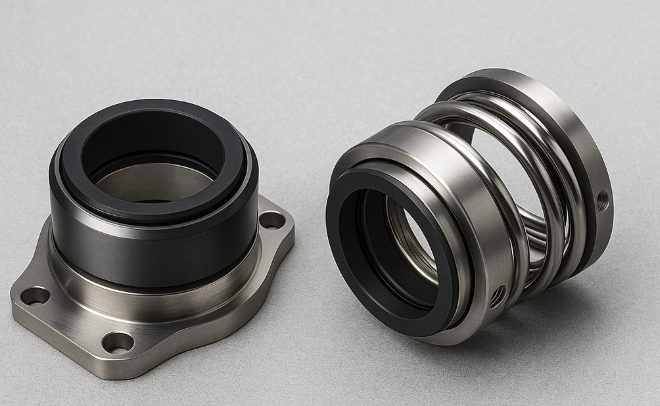
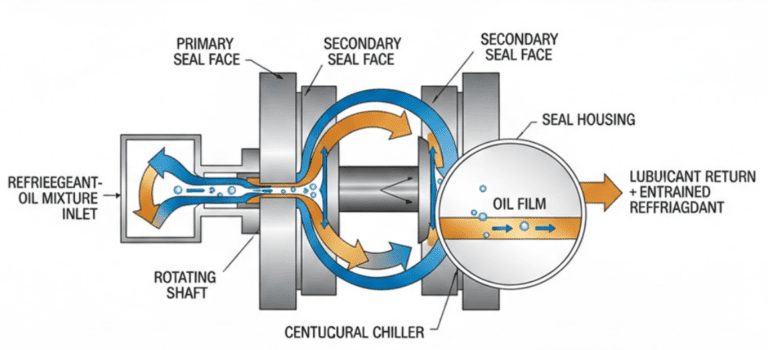
API 682 is another standard developed by the American Petroleum Institute that focuses specifically on shaft sealing systems for centrifugal and rotary pumps used in the petroleum, natural gas, and chemical industries. This standard provides guidelines for the selection, design, specification, and testing of sealing systems.
The purpose of API 682 is to improve the reliability and performance of sealing systems, which are critical components in pumps that prevent leakage and maintain process safety. The standard covers various types of sealing systems, including single and dual mechanical seals, as well as gas seals and barrier fluid systems.
API 682 provides a structured approach to seal selection based on the fluid properties, operating conditions, and environmental factors. It also establishes requirements for materials, design features, and manufacturing processes to ensure the sealing system’s compatibility with the pumped fluid and the operating environment.
The standard includes provisions for testing and qualification of sealing systems, including performance tests, endurance tests, and compatibility tests with the pumped fluid. API 682 also provides guidelines for the installation, operation, and maintenance of sealing systems to optimize their performance and extend their service life.
By specifying the requirements for sealing systems, API 682 complements API 610 in ensuring the overall reliability and safety of pumping systems in the oil, gas, and chemical industries.
Difference Between API 610 and API 682
Scope
API 610 encompasses a broader range of centrifugal pumps, including overhung pumps, between bearings pumps, and vertically suspended pumps. It covers pumps used in various applications, such as process services, boiler feed, water injection, and pipeline service.
In contrast, API 682 specifically focuses on shaft sealing systems for centrifugal and rotary pumps. It provides guidelines for the design, selection, and operation of sealing systems, including mechanical seals, seal supply systems, and auxiliary piping plans.
Technical Focus
API 610 primarily addresses the design, materials, manufacturing, testing, and documentation requirements for centrifugal pumps. It specifies criteria for pump types, configurations, pressure ratings, materials of construction, and performance testing to ensure reliability and safety in operation.
API 682, on the other hand, concentrates on the technical aspects of sealing systems. It defines seal categories, arrangements, and configurations based on the service conditions and fluid properties. The standard also provides detailed specifications for seal materials, design features, and performance testing to ensure seal integrity and minimize leakage.
Relationship
API 610 and API 682 are closely related and often used together in industry. Pumps built to API 610 standards frequently incorporate seal systems designed to API 682 specifications. The two standards are complementary, with API 610 covering the pump itself and API 682 addressing the critical sealing interfaces.
Many pumps conforming to API 610 will reference API 682 for seal system requirements. Using both standards together helps ensure a well-integrated and reliable pumping system suitable for demanding process industry applications.
Design and Construction
From a design and construction standpoint, API 610 provides detailed specifications for centrifugal pump components such as casings, impellers, shafts, bearings, wear rings, and more. It covers different pump types like overhung pumps, between-bearing pumps, and vertically suspended pumps. The standard also specifies requirements for materials, fabrication, welding, and NDE.
In terms of seal design and construction, API 682 gives requirements for seal types, materials, faces, geometry, and support systems. It categorizes seals into arrangements and configurations based on factors like seal orientation, number of seals, and buffer/barrier fluid setups. The standard also covers instrumentation, piping plans, and auxiliary equipment needed for reliable seal operation.