What Is Plan 52
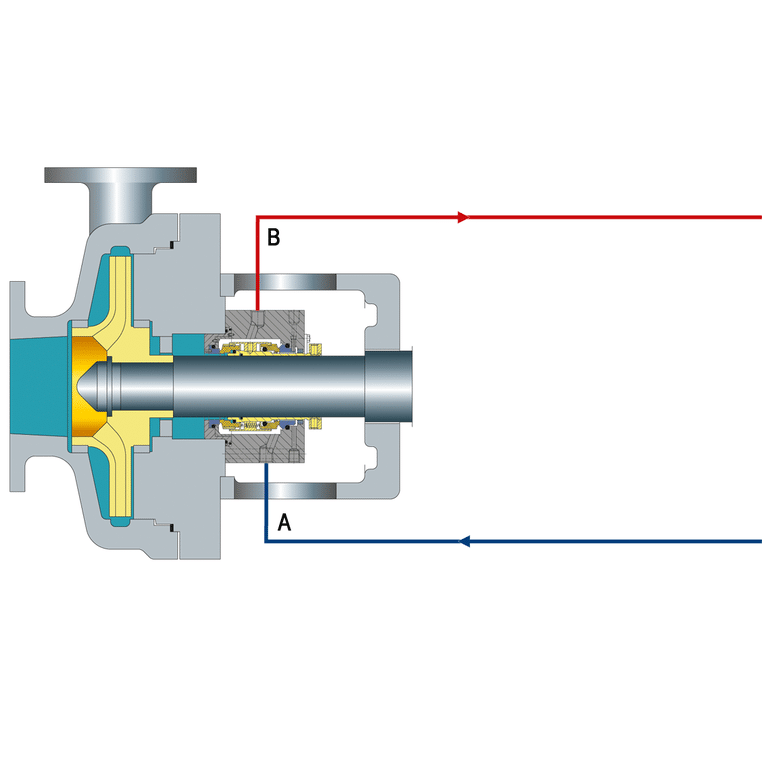
Plan 52 is a popular piping plan used in mechanical seals to control the environment around the seal faces. This plan involves using an external fluid reservoir to provide a clean, cool, and compatible barrier fluid to the seal chamber. The barrier fluid is maintained at a pressure higher than the process fluid, preventing process fluid from entering the seal chamber and causing damage to the seal faces.
In Plan 52, the barrier fluid is circulated through the seal chamber using a pumping ring or other circulation device. The circulation helps to remove heat generated by the seal faces and keeps the barrier fluid clean and free of contaminants. The barrier fluid is then cooled and filtered in the external reservoir before being recirculated back to the seal chamber.
Key Features of Plan 52
- External reservoir for buffer fluid circulation
- Buffer fluid maintained at a higher pressure than the sealed fluid
- Provides lubrication and cooling to the seal faces
- Prevents contaminant ingress into the seal chamber
- Suitable for single mechanical seals
When to Use Plan 52
- The process fluid is clean and non-abrasive
- The seal faces require additional lubrication and cooling
- Contamination of the process fluid must be prevented
- A single mechanical seal is sufficient for the application
What Is Plan 53
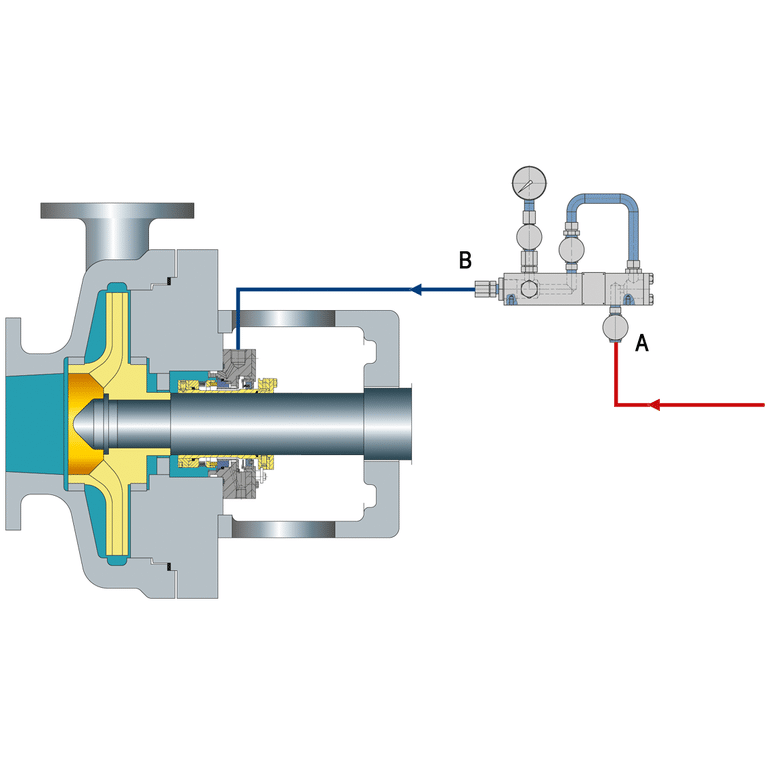
Plan 53 is a piping plan used in mechanical seals to provide barrier fluid circulation and pressurization for the seal chamber. This plan is designed to maintain a higher pressure in the seal chamber compared to the process fluid, preventing process fluid from entering the seal chamber and causing damage to the seal faces. Plan 53 is commonly used in applications where the process fluid is hazardous, toxic, or contains abrasive particles that could harm the seal faces.
The barrier fluid used in Plan 53 is typically a clean, compatible liquid that is immiscible with the process fluid. The barrier fluid is pressurized using an external source, such as a bladder accumulator or a piston accumulator, which maintains a constant pressure in the seal chamber. The barrier fluid is circulated through the seal chamber using a pumping ring or other circulation device, ensuring that the seal faces are constantly lubricated and cooled.
Types of Plan 53
Plan 53a
Plan 53a is the most basic version of Plan 53, featuring a pressurized barrier fluid reservoir maintained at a pressure higher than the seal chamber pressure. This arrangement ensures that the barrier fluid consistently flows into the seal chamber, preventing process fluid from entering the barrier fluid system. The barrier fluid is typically a clean, compatible liquid that lubricates and cools the seal faces while providing a positive pressure differential across the seal.
Plan 53b
Plan 53b builds upon Plan 53a by incorporating a bladder accumulator in the barrier fluid system. The bladder accumulator maintains a constant pressure on the barrier fluid, compensating for any thermal expansion or contraction of the fluid during operation. This enhancement helps to minimize pressure fluctuations and ensures a stable flow of barrier fluid to the mechanical seal, even under varying temperature conditions.
Plan 53c
Plan 53c is the most advanced version of Plan 53, featuring a piston accumulator instead of a bladder accumulator. The piston accumulator provides a more robust and reliable means of maintaining constant pressure on the barrier fluid, particularly in high-pressure applications. In Plan 53c, the barrier fluid is separated from the pressurizing gas by a moving piston, which adjusts its position to maintain the desired pressure level. This configuration offers superior pressure control and allows for a wider range of operating pressures compared to Plan 53a and Plan 53b.
Key Features of Plan 53
- Dual mechanical seal arrangement with pressurized barrier fluid
- Provides enhanced sealing performance and reliability
- Barrier fluid acts as a lubricant, coolant, and positive pressure differential
- Variations available for different application requirements (53a, 53b, 53c)
- Suitable for high-temperature, high-pressure, or critical service applications
When to Use Plan 53
- Enhanced sealing performance and reliability are required
- The process fluid is hazardous, toxic, or expensive
- High-temperature or high-pressure conditions are present
- Zero leakage to the atmosphere is critical
- Regulatory compliance mandates the use of dual seals (e.g., API 682)