If you work in maintenance or plant operations, you’ve probably faced this choice: should I use a gland packing seal or a mechanical seal for this pump?
The truth is simpler than you’d think. Gland packing and mechanical seals are fundamentally different technologies that solve the same problem in opposite ways. One trades reliability for affordability. The other trades upfront cost for years of trouble-free operation.
How Do Gland Packing Seals Work?
Basic Construction and Components
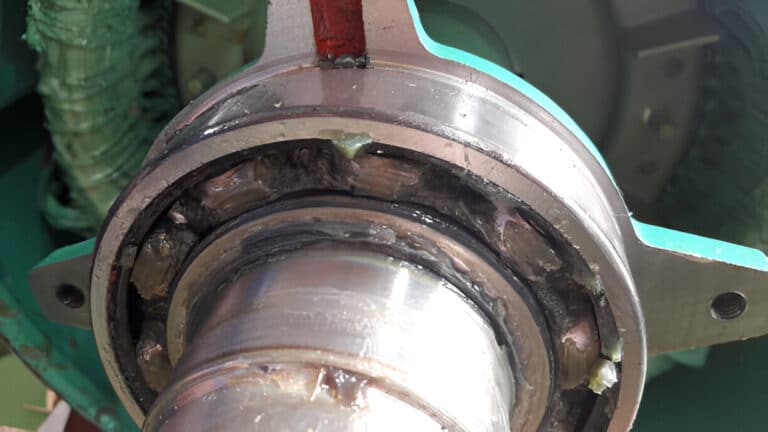
Gland packing is the older, simpler technology. It uses braided rope-like material wound around your pump shaft. The material itself comes in different flavors: graphite, PTFE (Teflon), Kevlar, or synthetic fibers. You pack these rings into a special chamber called the stuffing box, which wraps around the rotating shaft.
That’s where the name comes from. A gland follower (or gland nut) sits on top of this material and gets progressively tightened to compress the packing. Think of it like packing a suitcase: as you compress it, it molds to fill all the empty spaces.
The beauty of this design is its simplicity. There are no precision-engineered parts. No specialized tools required. Just rope-like material, a chamber, and a wrench.
Operating Principles
Here’s the magic: when you tighten the gland follower, it pushes down vertically. This vertical (axial) pressure transforms into horizontal (radial) pressure, forcing the packing material to hug the shaft tightly from all sides.
Gland packing actually seals through two mechanisms working together. The first is the labyrinth effect. Pressurized fluid trying to escape doesn’t find a straight path. Instead, it winds through countless tiny gaps in the packing material, losing pressure and speed with each turn. Like trying to run through a maze instead of a hallway.
The second mechanism is a thin lubrication film. Here’s the counterintuitive part: properly adjusted packing must leak slightly. It’s not a design flaw. It’s essential. That small amount of leakage (typically 8-15 drops per minute) lubricates the contact between packing and shaft, carries away frictional heat, and keeps the packing flexible.
If your packing doesn’t leak at all, it’s actually starving. It will dry out, harden, and fail faster. If it leaks excessively, you need to tighten it.
How Do Mechanical Seals Work?
Core Design and Components
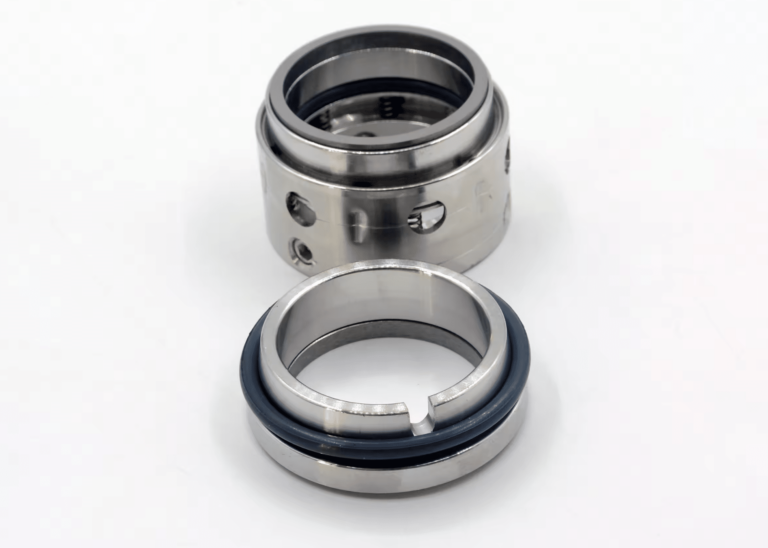
Mechanical seals take a completely different approach. Instead of compressed fiber, you get precision engineering. The seal has two primary faces: one rotating (attached to your shaft) and one stationary (attached to the pump housing). These faces are machined with such precision that they’re flat within just 2 light bands—essentially micrometer-level flatness.
A spring or bellows mechanism pushes these faces together with consistent force. Secondary sealing elements (usually O-rings or gaskets) seal the gaps where the seal assembly connects to the shaft and housing. Everything works together to create a near-perfect barrier against leakage.
The sealing faces themselves are made from different materials depending on your application. A common combination is a hard material like silicon carbide on one face and soft carbon on the other. Hard and soft together minimize wear while maintaining a tight seal.
Operating Principles
When your pump runs, these two precision faces stay in contact under spring pressure. A thin film of liquid between them—just a few microns thick—provides the actual seal. This liquid film is crucial. It cools the seal, lubricates the faces, and prevents them from welding together.
Unlike packing, mechanical seals are designed for near-zero leakage. Properly installed and maintained, they leak in milliliters per hour, not drops per minute. Some configurations leak almost nothing at all.
Key Differences: A Practical Comparison
| Characteristic | Gland Packing | Mechanical Seal |
|---|---|---|
| Leakage Rate | 10-20 drops/min (required for operation) | Milliliters per hour (near zero) |
| Typical Service Life | 1-2 years | 1-3 years (often 3-8 years) |
| Initial Cost | Low ($50-200) | High ($300-500+) |
| Installation Complexity | Simple, field-installable | Complex, requires alignment tools |
| Maintenance Interval | Frequent (monthly adjustments) | Minimal (annual checks) |
| Maintenance Type | Gland tightening, replacement | Monitoring, filter changes |
| Energy Consumption | High (baseline) | Low (6x more efficient) |
| Temperature Range | Up to 550°C | Typically 400-500°C |
| Pressure Handling | Up to 140 BAR | Higher, depends on design |
| Shaft Wear | Significant over time | Minimal with proper filtration |
| Adaptation to Misalignment | Good tolerance | Limited tolerance |
Advantages of Gland Packing Seals
When Gland Packing Is Your Best Choice
Gland packing earns its place in the market by being straightforward and forgiving. You should choose gland packing when your situation matches these criteria:
You’re sealing water or non-toxic liquids. If your pump handles municipal water, cooling water, or other benign fluids where small amounts of leakage won’t cause problems, packing is economical. The small controlled leakage isn’t an environmental or safety concern.
Your application tolerates some leakage. Not all processes require zero leakage. If your equipment can handle 10-15 drops per minute without operational issues, packing works fine. You capture or contain that leakage safely.
Your equipment has significant shaft movement or misalignment. Some pumps and agitators experience radial shaft movement or aren’t perfectly aligned. Gland packing adapts to this movement. The flexible material compresses and decompresses as the shaft moves. Mechanical seals have tighter tolerances and don’t handle this scenario as well.
You need quick, field-level repairs. When your seal fails on a Saturday night, you don’t want to wait for specialized technicians. Gland packing replacement takes an hour with basic tools. Your maintenance crew can handle it themselves. You need to have replacement packing in stock, but it costs dollars, not hundreds of dollars.
Your budget is severely constrained. Gland packing costs a fraction of mechanical seals. If you’re upgrading 20 old pumps and budget is tight, packing gets you operational sealing at low cost.
Advantages of Mechanical Seals
When Mechanical Seals Are Worth the Investment
Mechanical seals cost more upfront. But they deliver value through reliability and efficiency. Choose mechanical seals when:
You’re handling hazardous, flammable, toxic, or expensive fluids. If your pump handles acetone, benzene, or pharmaceutical compounds where leakage contaminates soil or groundwater, you need near-zero leakage. Mechanical seals deliver this. The environmental liability and cleanup costs of packing leakage would dwarf the seal investment.
Your process absolutely prohibits leakage. Pharmaceutical manufacturing, food processing, and semiconductor production have zero-leakage requirements. Mechanical seals are the only acceptable choice here.
You’re running high-temperature or high-pressure applications. As temperature and pressure increase, gland packing deteriorates faster. Mechanical seals handle these extremes better. You’ll see mechanical seals in hot oil circulation, high-pressure injection, and steam pump applications.
You need long operational life with minimal downtime. Mechanical seals last 3-8 years on average. You’ll change them out once, maybe twice, during the life of the equipment. Gland packing requires replacement every 1-2 years. Over a 10-year period, you’re replacing packing 5-10 times versus 1-3 times for seals. That’s downtime you eliminate.
You have high utility costs. Gland packing consumes 6 times more power than a balanced mechanical seal. If you’re running equipment 24/7, that difference adds up to thousands of dollars per year. Many mechanical seal upgrades pay for themselves through energy savings in 6-12 months.
You want to eliminate constant maintenance adjustments. With packing, you’re adjusting gland nuts monthly (or more often in harsh conditions). With mechanical seals, you check them quarterly during routine maintenance. This frees your maintenance team for other work.
How to Choose Between Them
Decision Criteria Checklist
Before you choose, answer these questions:
1. What fluid are you sealing?
Water or benign liquid → Gland packing acceptable
Hazardous, toxic, flammable, or expensive → Mechanical seal required
2. What’s your leakage tolerance?
Small amounts acceptable → Gland packing
Zero leakage required → Mechanical seal
3. What are your operating conditions?
Moderate temperature and pressure → Either can work
High temperature or high pressure → Mechanical seal
Significant shaft movement → Gland packing
4. How often can you do maintenance?
Monthly adjustments acceptable → Gland packing
Minimize maintenance → Mechanical seal
5. What’s your budget?
Upfront cost critical → Gland packing
Total cost of ownership critical → Mechanical seal
6. How long do you need the equipment to run without replacement?
1-2 years acceptable → Gland packing
3+ years required → Mechanical seal
7. Do you have environmental or safety regulations?
EPA or regulatory restrictions on leakage → Mechanical seal
No restrictions → Either works
Real-World Selection Guide
Use these scenarios to make your choice:
Choose Gland Packing If:
- Sealing municipal water systems, cooling water, or general non-toxic liquids
- Equipment has radial shaft movement or can’t be perfectly aligned
- Budget is extremely tight and upfront cost is the deciding factor
- Your maintenance team has limited mechanical seal experience
- Leakage can be captured in a drain or containment system
- Equipment operates intermittently
Choose Mechanical Seals If:
- Sealing petroleum products, solvents, or specialty chemicals
- Sealing pharmaceutical, food processing, or clean room applications
- Equipment runs continuously 24/7
- Operating temperatures exceed 200°C or pressures exceed 100 PSIG
- Long intervals between maintenance are required
- Energy costs are significant
- Environmental liability for leaks is high
Cost Analysis: Long-Term ROI
Breaking Down the Expenses
Material Costs:
A basic gland packing set runs $50-150. Premium PTFE packing runs $150-250. A mechanical seal costs $300-500, sometimes more depending on type and material.
Initial advantage: gland packing, 3-5x cheaper.
Installation Labor:
Gland packing installation takes 2-4 hours with basic tools. Most maintenance crews can do this. You’re looking at $100-200 in labor.
Mechanical seal installation takes 6-8 hours and often requires alignment specialists. You’re looking at $400-800 in labor (sometimes more if the equipment needs disassembly).
Initial advantage: gland packing by significant margin.
Maintenance Labor:
Here’s where things flip. Gland packing requires monthly or quarterly maintenance. You’re adjusting gland nuts, monitoring temperature, eventually replacing the packing. Over 5 years, you’ll spend 30-50 hours on maintenance and 1-2 replacements. That’s roughly $1,500-2,500 in labor plus material costs.
Mechanical seals require quarterly inspections (1-2 hours per year) and occasional maintenance. Over 5 years, you’ll spend 4-8 hours on maintenance. That’s roughly $200-400 in labor. You might replace the seal once.
Energy Costs:
Gland packing uses 6 times more power than a mechanical seal on identical equipment. If you’re running a 10 kW pump continuously, that’s about 0.6 kW wasted. At $0.10/kWh and 8,760 hours per year, that’s roughly $525/year in wasted energy for one pump.
Over 5 years on one pump: $2,625 in excess energy costs. Multiply this across multiple pumps and the number becomes staggering.
Leakage and Product Loss:
Gland packing leaks 10-20 drops per minute. That’s roughly 15-30 liters per day. If you’re pumping a $5/liter fluid, that’s $75-150 per day in lost product. Over a year, that’s $27,000-55,000 in lost product from a single pump.
Mechanical seals leak milliliters per hour. The product loss is negligible.
Making the Financial Decision
Let’s run real numbers for a typical scenario: a single circulation pump running 8,000 hours per year for 5 years on a water-compatible, but slightly corrosive, industrial fluid.
Gland Packing Route:
- Initial installation: $250
- Maintenance labor (5 years): $1,500
- Packing replacements (4 replacements): $600
- Energy waste: $2,625
- Product loss: $27,500
- Total 5-year cost: $32,475
Mechanical Seal Route:
- Initial installation: $700
- Maintenance labor (5 years): $300
- Seal replacement (1 replacement): $500
- Energy waste: $0
- Product loss: $0
- Total 5-year cost: $1,500
In this scenario, mechanical seals save $30,975 over five years despite costing $400 more upfront.
The crossover point varies by application, but the math strongly favors mechanical seals in most industrial settings once you account for all costs.
Conclusion
Gland packing and mechanical seals are fundamentally different solutions to the same problem. Gland packing is simple, inexpensive upfront, and forgiving of equipment imperfections. Mechanical seals are complex, costly to install, and sensitive to contamination and misalignment, but deliver reliability and efficiency.
Your choice should match your situation. If you’re sealing water in a low-cost application where leakage is acceptable, gland packing is perfectly reasonable. If you’re sealing expensive, hazardous, or temperature-sensitive fluids in a high-cost operation, mechanical seals are almost always the right economic choice when you calculate total cost of ownership.




