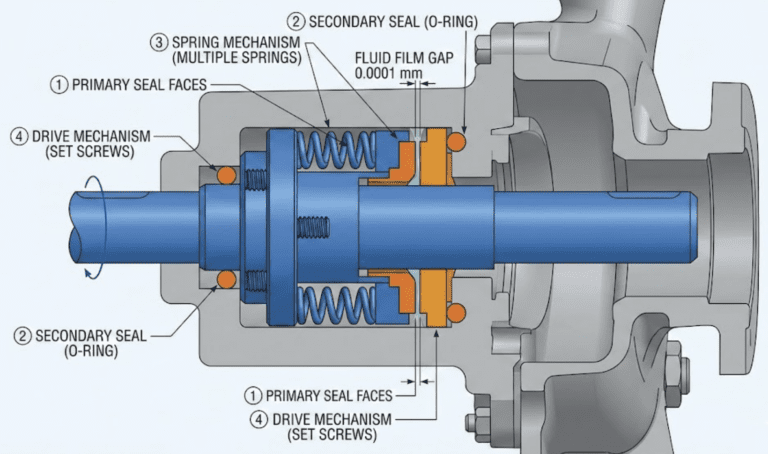
Are you struggling to determine the correct size of gland packing for your machinery? Using the wrong size packing can lead to leaks, equipment damage, and costly downtime.
Don’t let improper packing sizing derail your operations. Incorrectly sized packing will fail prematurely, requiring frequent replacement. Leaks can contaminate products, create safety hazards, and waste valuable resources.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the simple process to accurately measure your equipment and calculate the optimal gland packing size. You’ll learn how to determine the packing cross-section and number of rings using just the shaft diameter and stuffing box depth. We’ve even included handy reference charts.
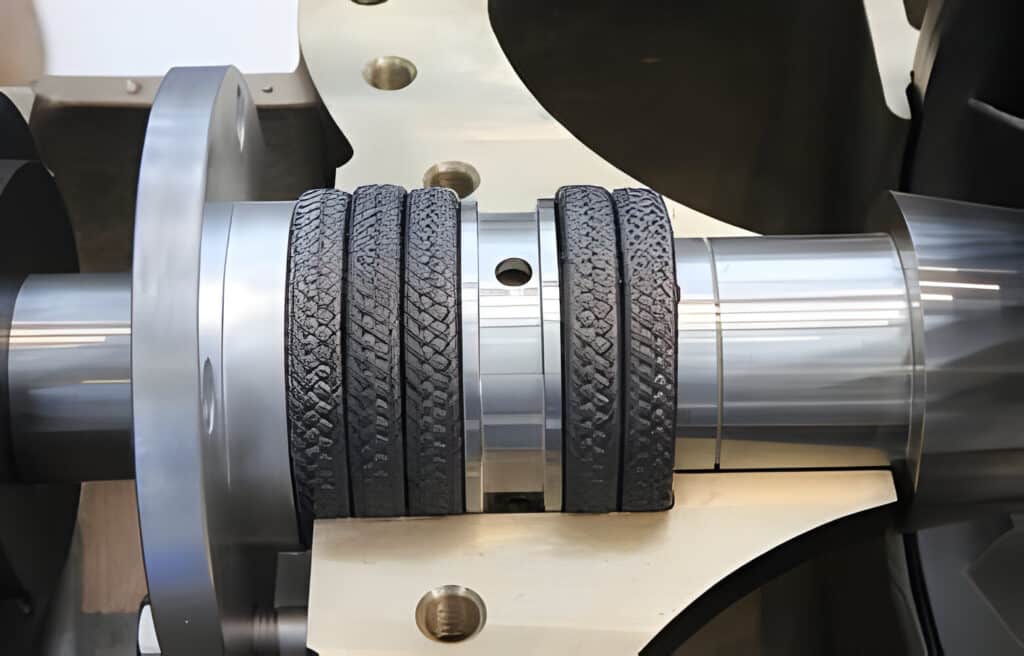

Measuring Shaft Diameter
Use a caliper or micrometer to measure the shaft at the point where it passes through the stuffing box. Take measurements at several points around the shaft circumference and calculate the average for the most precise sizing.
If the shaft is worn, pitted or corroded, measure the diameter at the widest point. The packing must be sized to accommodate the largest shaft diameter to ensure a proper seal.
Measuring Stuffing Box Depth
Next, measure the depth of the stuffing box cavity. This is the space where the packing will be installed. Insert the depth gauge of a caliper into the stuffing box until it touches the bottom.
The recommended stuffing box depth is typically 6-8 times the cross-sectional size of the packing. So a 3/8″ packing would require a 2-1/4″ to 3″ deep stuffing box. A stuffing box that is too shallow will not allow enough packing rings to be installed.
Calculating Gland Packing Size
With the shaft diameter and stuffing box depth measurements, you can now calculate the appropriate gland packing size. There are two key factors to determine – the packing cross-section and the number of packing rings required.
Calculate the packing cross-section
The packing cross-section is determined by this formula:
Packing Cross-Section = (Stuffing Box Bore – Shaft Diameter) / 2
For example, if the stuffing box bore measures 2.125″ and the shaft diameter is 1.375″:
(2.125″ – 1.375″) / 2 = 0.375″
So in this example case, a 3/8″ cross-section packing would be selected. Standard packing cross-sections come in 1/8″ increments such as 1/4″, 3/8″, 1/2″, 5/8″, etc. Always round to the nearest standard size.
Determine the number of packing rings
The goal is to fill the stuffing box cavity to a depth of about 1″ less than the total depth. You can calculate the number of rings by this formula:
Number of Rings = (Stuffing Box Depth – 1″) / Packing Cross-Section
Continuing with the example of a 3″ stuffing box depth and 3/8″ cross-section packing:
(3″ – 1″) / 0.375″ = 5.33
Round to the nearest whole number, so 5 rings of 3/8″ cross-section packing would be used in this case.
Gland Packing Size Charts
| Shaft Size (inches) | Suggested Packing Size (inches) |
|---|---|
| 3/4″ | 1/8″ |
| 7/8″ or 1″ | 3/16″ |
| 1 1/8″ or 1 1/4″ | 1/4″ |
| 1 3/8″ or 1 3/4″ | 5/16″ |
| 2″ or 2 1/8″ | 3/8″ |