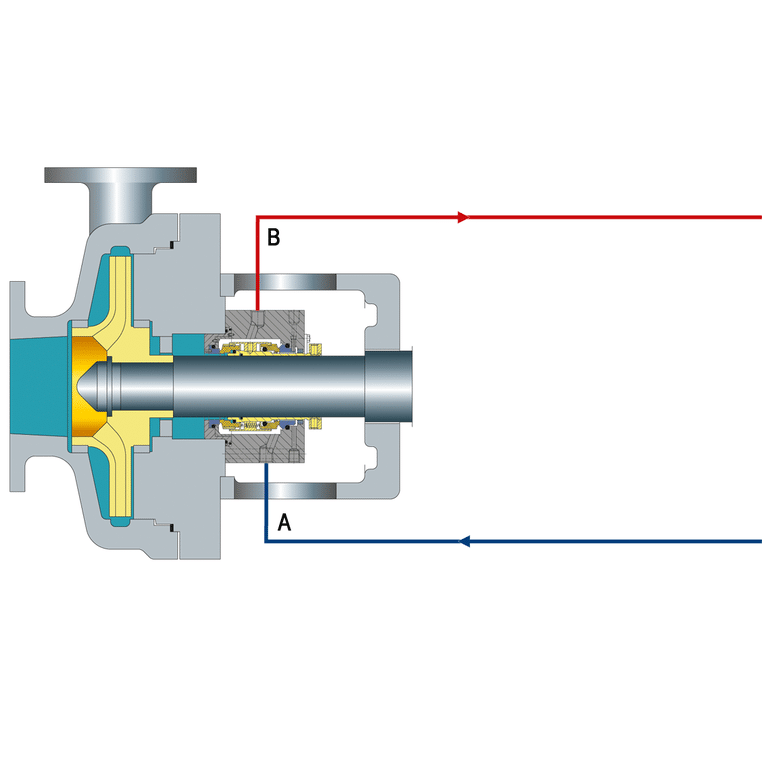
What is Gland Packing
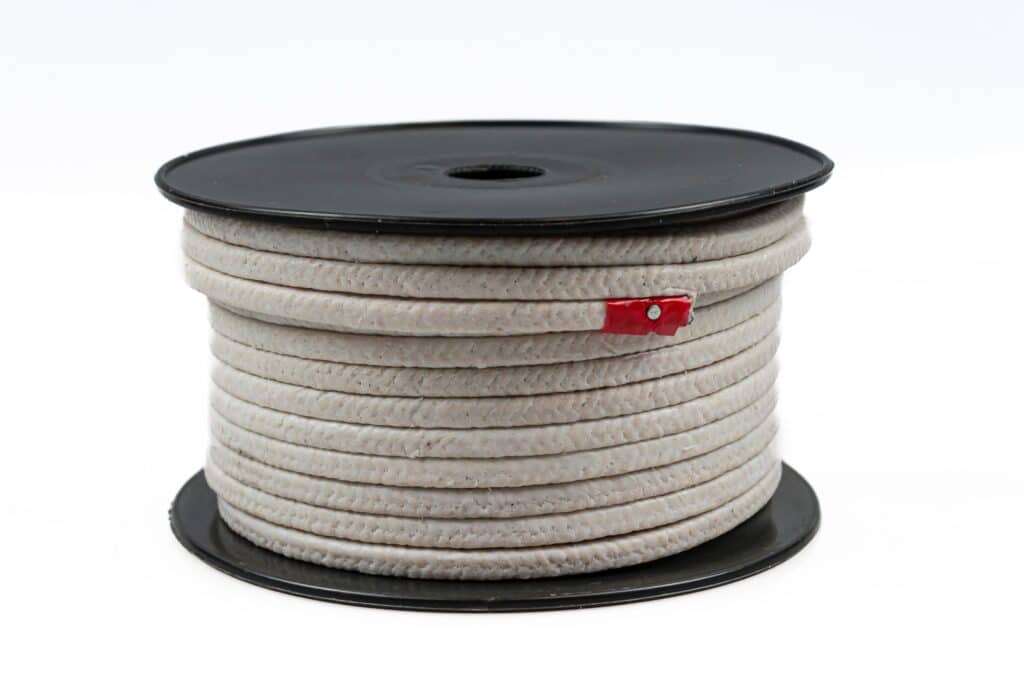
Gland packing, also known as compression packing, is a type of mechanical seal consisting of soft, pliable materials such as braided fibers, graphite, or PTFE. It is commonly used to seal rotating or reciprocating shafts in pumps, valves, and other industrial equipment. The packing material is compressed into the stuffing box, creating a tight seal around the shaft to prevent leakage of fluids or gases.
Advantages of Gland Packing
- Versatility: Gland packing can be used in a wide range of applications, including high-temperature and high-pressure environments.
- Cost-effective: Compared to other sealing methods, gland packing is relatively inexpensive and easy to replace.
- Adaptability: The soft, pliable nature of gland packing allows it to conform to irregularities in the shaft or stuffing box, providing an effective seal.
- Easy maintenance: Gland packing can be adjusted or tightened as needed to compensate for wear, extending its service life.
Disadvantages of Gland Packing
- Higher friction: Gland packing creates more friction against the rotating shaft compared to other sealing methods, which can lead to increased energy consumption and wear on the shaft.
- Leakage: A small amount of leakage is often necessary to lubricate and cool the packing, which can be problematic in applications where zero leakage is required.
- Regular maintenance: Gland packing requires periodic adjustment and replacement to maintain an effective seal, which can be time-consuming and costly.
- Limited speed: Gland packing is not suitable for high-speed applications due to increased friction and heat generation.
When to Use Gland Packing
Gland packing is an appropriate choice for sealing in the following situations:
- Low to medium-speed applications where a small amount of leakage is acceptable.
- High-temperature or high-pressure environments where other sealing methods may not be suitable.
- Applications requiring frequent adjustment or replacement of the sealing material.
- Equipment with worn or damaged shafts that cannot be easily repaired or replaced.
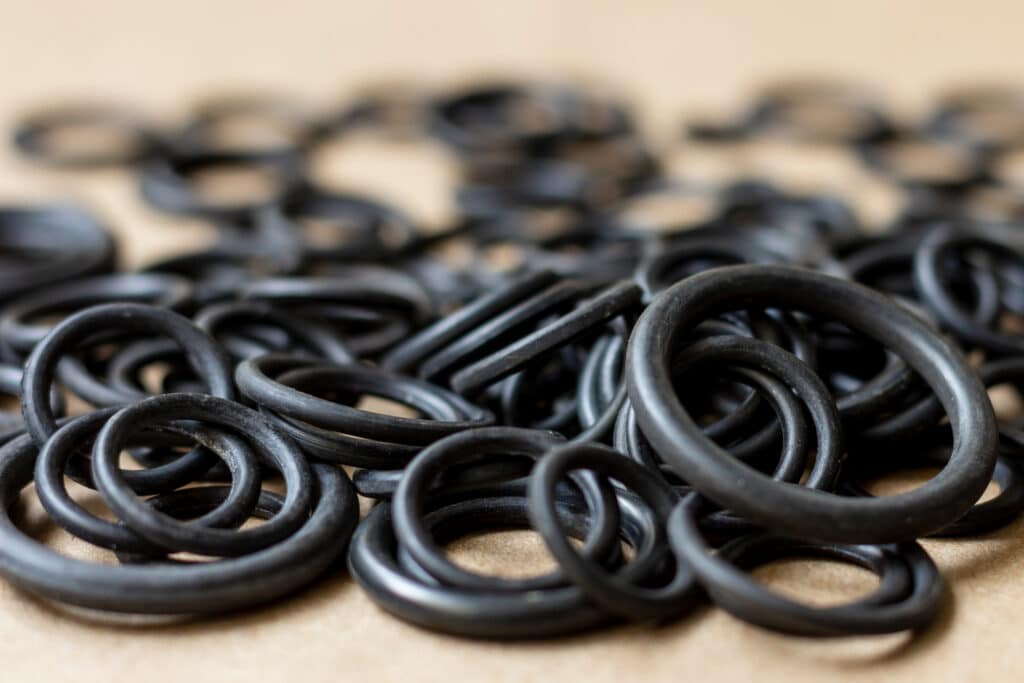

What is O-Ring
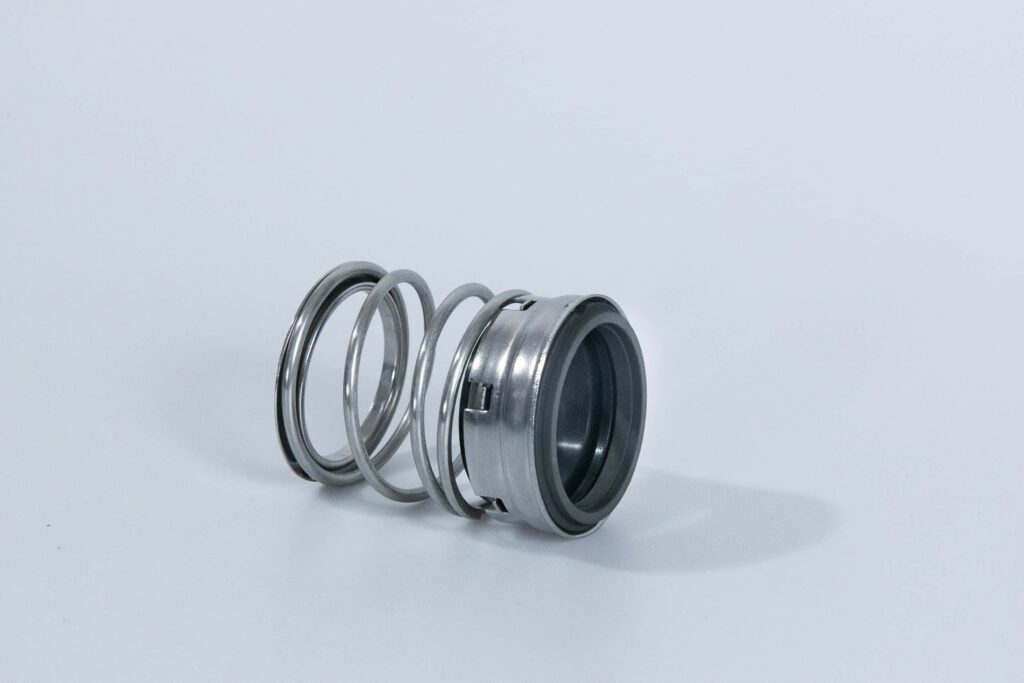
An O-ring is a type of mechanical seal made from an elastomeric material, typically rubber or a synthetic polymer such as nitrile or Viton. It has a circular cross-section and is designed to be seated in a groove, creating a tight seal between two mating surfaces. O-rings are widely used in various industries to prevent leakage of fluids or gases in static and dynamic applications.
Advantages of O-Ring
- Excellent sealing performance: O-rings provide a highly effective seal due to their elastomeric properties, which allow them to conform to mating surfaces and maintain sealing integrity under pressure.
- Low friction: Unlike gland packing, O-rings create minimal friction, reducing wear on mating surfaces and improving energy efficiency.
- Compact design: O-rings require less space compared to other sealing methods, making them ideal for applications with limited space.
- Wide compatibility: O-rings are available in a variety of materials, allowing them to be used with a wide range of fluids and in various temperature and pressure conditions.
Disadvantages of O-Ring
- Limited temperature range: The performance of O-rings can degrade at extreme temperatures, with most materials suitable for use between -40°C and 200°C.
- Susceptibility to damage: O-rings can be damaged by improper installation, excessive compression, or exposure to incompatible fluids or contaminants.
- Higher initial cost: Compared to gland packing, O-rings and their associated grooves can be more expensive to manufacture and install.
- Difficulty sealing irregular surfaces: O-rings may not provide an effective seal on heavily worn or irregular surfaces, as they require a smooth, consistent sealing surface.
When to Use O-Ring
O-rings are the preferred choice for sealing in the following situations:
- Applications requiring minimal leakage and low friction, such as hydraulic and pneumatic systems.
- High-speed rotating equipment where low friction and minimal wear are essential.
- Static sealing applications, such as flanged connections or valve bonnets.
- Environments with moderate temperature and pressure conditions, compatible with the O-ring material.