In the world of mechanical seals, various components work together to ensure optimal performance and reliability. One such component is the throat bushing, a critical element that contributes to the smooth operation of mechanical seals in diverse applications.
This article will delve into the intricacies of throat bushings, exploring their functions, materials, applications, and maintenance aspects.
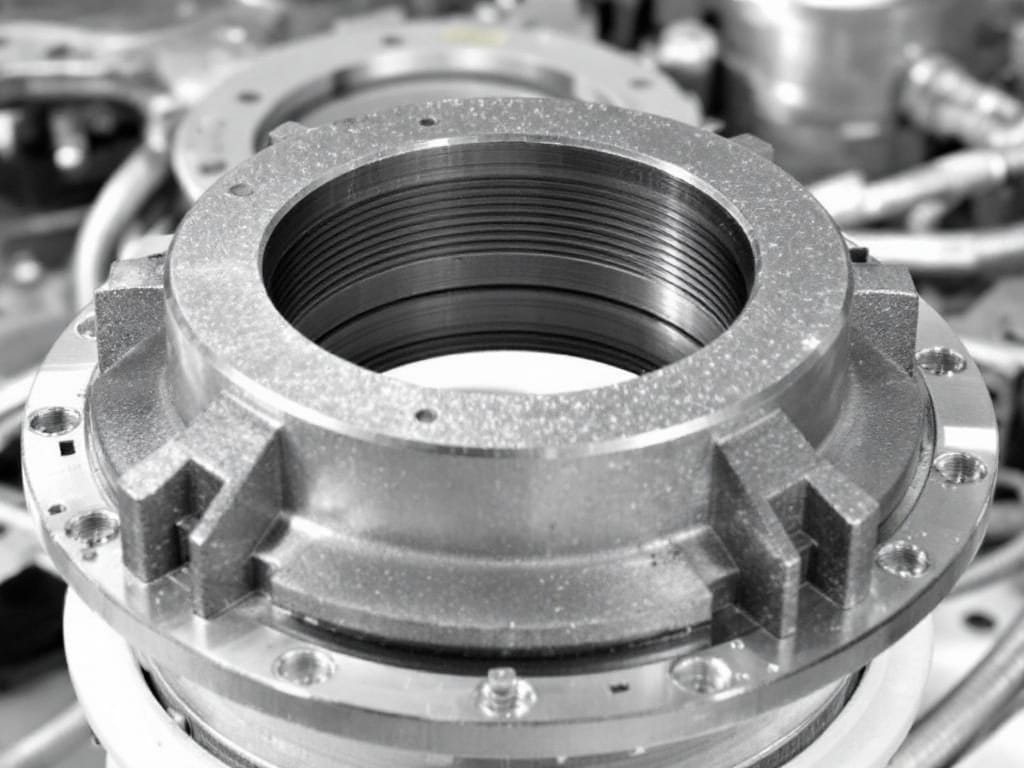

What Is a Throat Bushing
A throat bushing, also known as a shaft packing sleeve or seal chamber insert, is a critical component in mechanical seals. It is a cylindrical sleeve that fits into the seal chamber bore, surrounding the shaft or sleeve where it passes through the seal gland plate.
Throat bushings are designed to work in conjunction with mechanical seals to optimize sealing performance and extend seal life. They are typically made from materials that are compatible with the process fluid and the mechanical seal components, such as stainless steel, bronze, or engineered plastics.
The geometry of a throat bushing is precisely engineered to meet the specific requirements of the sealing application. Key dimensions include the inside diameter (ID), which matches the shaft or sleeve diameter; the outside diameter (OD), which fits into the seal chamber bore; and the length, which extends from the gland plate to the impeller or other rotating equipment.
How Throat Bushing Works
The primary function of a throat bushing is to create a controlled environment for the mechanical seal to operate in. It does this by managing the flow and pressure of the process fluid within the seal chamber.
When the shaft rotates, the process fluid is drawn into the seal chamber through the clearance between the shaft and the throat bushing ID. The fluid then flows through the annular space between the rotating shaft and the stationary throat bushing.
As the fluid passes through this restricted space, its velocity increases, creating a pressure drop across the throat bushing. This pressure drop helps to control the fluid flow rate and pressure within the seal chamber, preventing excessive turbulence and heat generation.
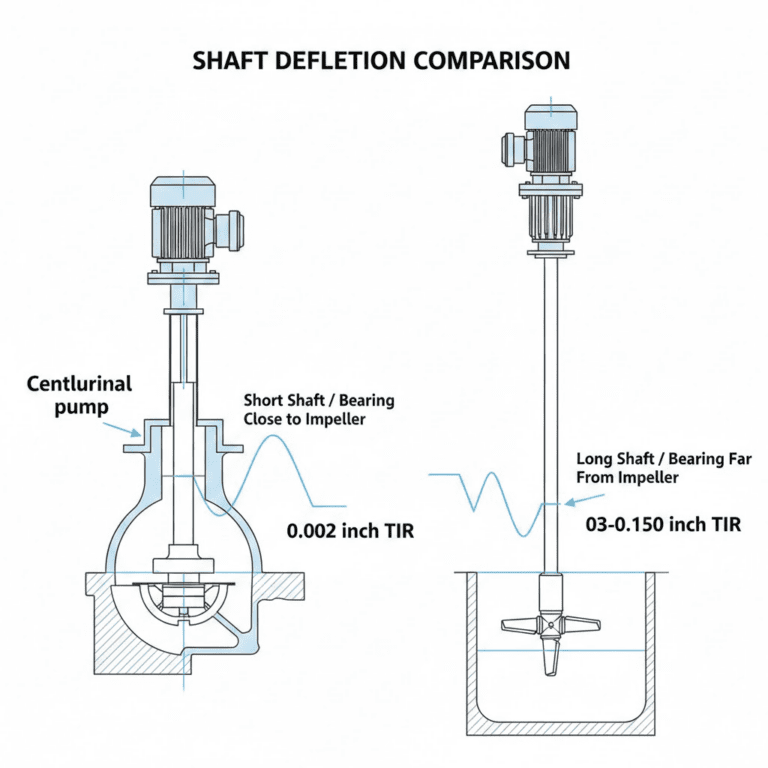
The throat bushing also helps to center the shaft within the seal chamber, providing a consistent running surface for the mechanical seal faces. This promotes even wear on the seal faces and helps to maintain proper alignment, which is critical for optimal sealing performance.
In some designs, the throat bushing may incorporate additional features such as flutes, grooves, or ports to further optimize the sealing environment. These features can help to promote fluid circulation, reduce stagnant areas, and facilitate the removal of heat and debris from the seal chamber.
Functions of a Throat Bushing
Flow Restriction
The throat bushing acts as a flow restrictor, limiting the amount of fluid that can enter the seal chamber from the process. By controlling the flow rate, the bushing helps maintain stable conditions within the sealing environment.
Pressure Management
In addition to restricting flow, the throat bushing also helps manage pressure within the seal chamber. By creating a controlled pressure drop across its length, the bushing ensures that the pressure at the seal faces remains within acceptable limits.
Sealing Environment Optimization
Throat bushings contribute to optimizing the sealing environment by influencing factors such as fluid velocity, temperature, and turbulence. By shaping the flow path and controlling fluid dynamics, the bushing helps create favorable conditions for the seal faces to operate effectively. This optimization can extend seal life, improve performance, and reduce the risk of premature failure.
Support for Flush Plans
Throat bushings play a vital role in supporting various flush plans used in mechanical seals. Flush plans are designed to introduce clean, compatible fluids into the seal chamber to cool, lubricate, and clean the seal faces. The throat bushing’s flow restriction and pressure management functions help ensure that the flush fluid is delivered at the appropriate rate and pressure, enhancing the effectiveness of the flush plan.
Materials Used for Throat Bushings
| Material | Characteristics | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Bronze | Good thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance | Water, mild chemicals |
| Stainless Steel | Excellent corrosion resistance, strength | Chemicals, pharmaceuticals |
| Hastelloy | Superior corrosion resistance, high-temperature stability | Aggressive chemicals, acids |
| Graphite | Self-lubricating, high-temperature resistance | High-temperature fluids, steam |
| PTFE | Low friction, chemical inertness | Chemicals, food processing |
Applications and Use Cases
Pumps
Throat bushings are widely used in centrifugal pumps to optimize seal performance and extend seal life. In pump applications, the bushing helps control the flow of process fluid into the seal chamber, reducing wear on the seal faces and minimizing leakage.
Mixers and Agitators
In mixing and agitation equipment, throat bushings help maintain stable sealing conditions despite the challenging fluid dynamics. The bushing’s flow restriction and pressure management functions are particularly important in these applications, where turbulence and varying fluid velocities can impact seal performance.
Compressors
Throat bushings are employed in compressor seals to control the flow of gas or refrigerant into the seal chamber. By restricting flow and managing pressure, the bushing helps prevent seal face contamination and maintains stable sealing conditions.
Reactors and Pressure Vessels
In high-pressure applications such as reactors and pressure vessels, throat bushings play a critical role in managing pressure at the seal faces. The bushing’s pressure-dropping capabilities ensure that the seal operates within its designed pressure limits, reducing the risk of seal failure or leakage.