Are you struggling to decide between gland packing seals and mechanical seals for your industrial machinery? Choosing the wrong seal can lead to costly leaks, excessive maintenance, and reduced efficiency.
Without a clear understanding of the differences between these two seal types, you risk making a decision that could negatively impact your operations. Leaks can cause environmental damage, while frequent seal replacements can drive up costs and downtime.
In this blog post, we’ll dive into the key differences between gland packing seals and mechanical seals. By examining factors like sealing mechanism, cost, leakage rates, maintenance needs, and more, you’ll gain the knowledge needed to select the optimal seal for your specific application.

What Is Gland Packing Seal
Gland packing seal, also known as compression packing, is a traditional sealing method used in pumps, valves, and other rotating equipment. It consists of soft, pliable materials like braided fibers or graphite that are compressed around the shaft to prevent fluid leakage. The packing material is housed in a stuffing box and adjusted using a gland follower to maintain proper compression.
What Is Mechanical Seal
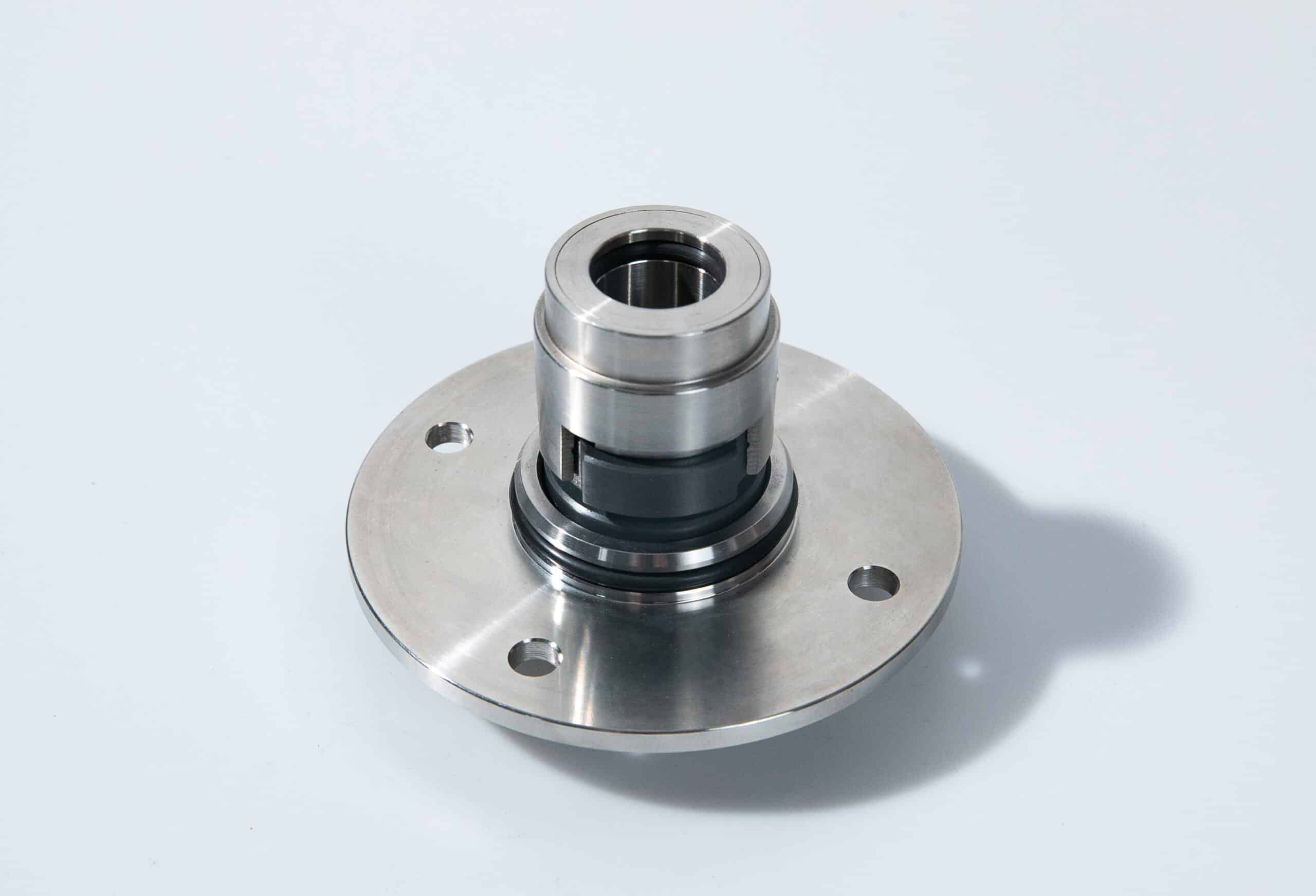
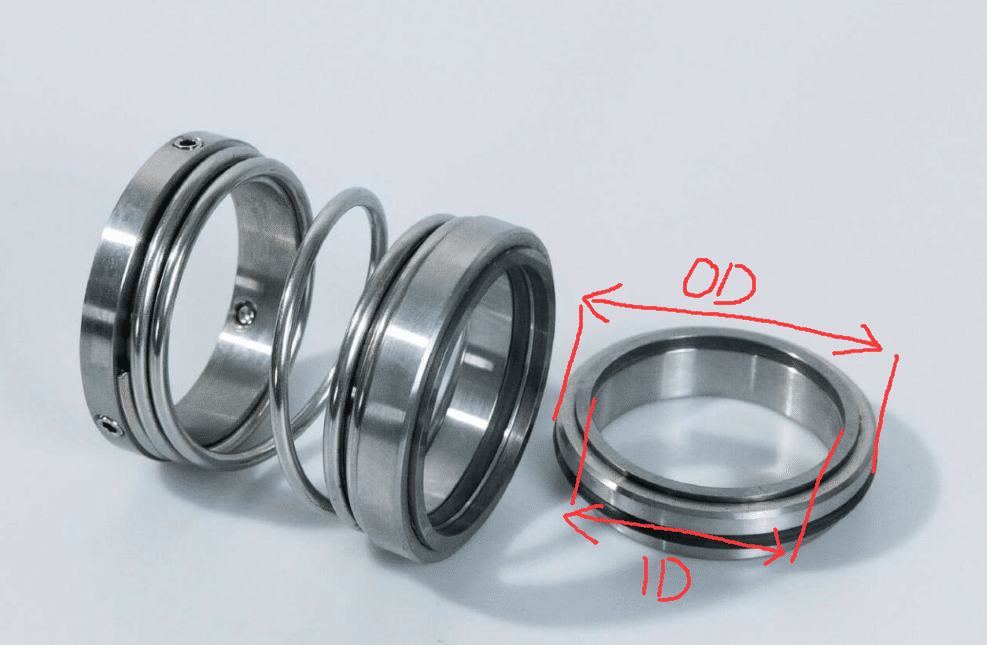
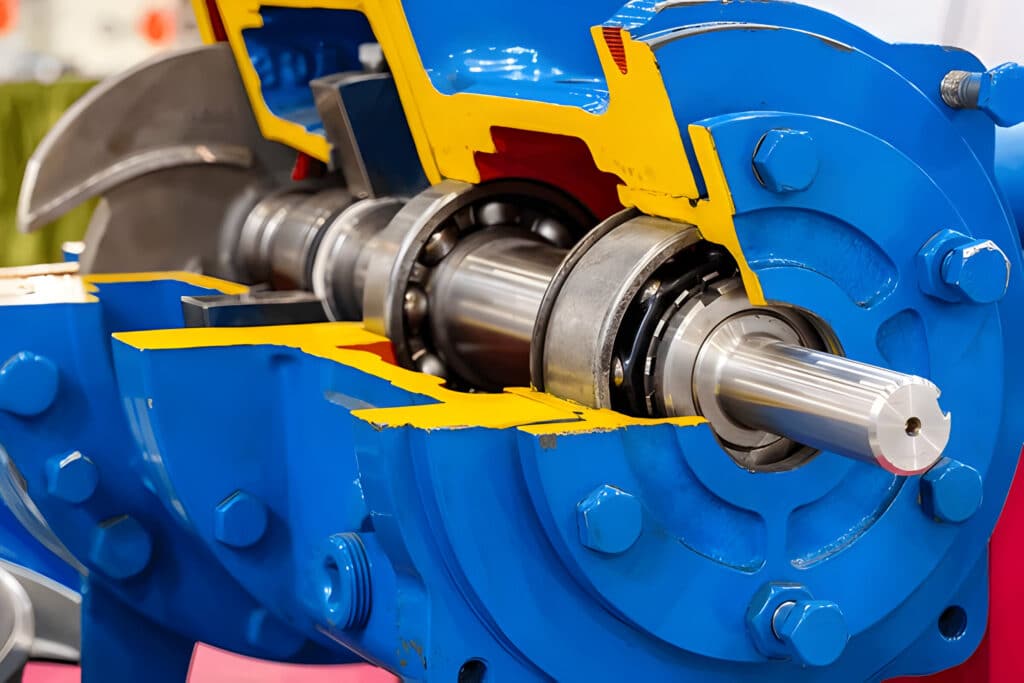
A mechanical seal is a modern sealing device that uses precision-engineered components to prevent leakage in rotating equipment. It consists of two main parts: a stationary component attached to the pump housing and a rotating component fixed to the shaft. The sealing surfaces are typically made of hard, wear-resistant materials like silicon carbide or tungsten carbide. A thin film of fluid between the sealing faces lubricates and cools the seal, preventing direct contact and minimizing wear.
Difference Between Gland Packing Seal and Mechanical Seal
Sealing Mechanism
Gland packing seals work by compressing packing material, typically braided from yarns like PTFE, graphite, or aramid fibers, around the shaft in the stuffing box. The compression of the packing material against the shaft and stuffing box walls creates the seal.
Mechanical seals utilize two flat sealing faces, one stationary and one rotating, that are pressed together by spring pressure and fluid pressure. A thin fluid film between the faces lubricates and seals the gap. Secondary seals like O-rings seal between the stationary and rotating components.
Cost
Gland packing is generally less expensive upfront compared to mechanical seals. The packing material itself is low cost and readily available.
Mechanical seals, while having a higher initial cost, often provide savings in the long run due to reduced leakage, longer service life, and improved efficiency.
Installation
Installing gland packing is relatively simple and can be done on-site by maintenance staff. It involves cutting rings of packing, staggering the joints, and manually compressing the packing into the stuffing box.
Mechanical seals have a more complex installation process that requires precise alignment and expert handling.
Leakage
Gland packing seals inherently allow a small amount of controlled leakage, which is necessary for lubrication and cooling. Typical leakage rates are around 1-10 drops per minute per inch of shaft diameter.
Mechanical seals are designed to operate with near-zero leakage, with typical rates less than 0.5 ml per hour.
Maintenance and Lifespan
Gland packing requires frequent adjustment to maintain the proper level of compression and leakage. The packing needs to be replaced periodically as it wears, typically every 6-12 months.
Mechanical seals, when properly selected and installed, require minimal maintenance until the end of their service life. However, when they do fail, the entire seal usually needs to be replaced, which is more involved than re-packing.
Energy Efficiency
Gland packing creates higher frictional losses compared to mechanical seals due to the contact between the packing and shaft. This friction consumes more energy and can lead to thermal issues.
Mechanical seals have much lower frictional losses thanks to the thin fluid film between the faces. This improves energy efficiency and reduces the heat load on the sealed system.
Liquid Compatibility
Mechanical seals offer superior liquid compatibility compared to gland packing seals. They can handle a wider range of liquids, including corrosive, toxic, and high-pressure fluids.
Gland packing seals are more limited in the types of liquids they can seal effectively. Certain corrosive or high-temperature fluids can degrade the packing material over time, leading to increased leakage. The weeping or dripping that is inherent in gland packing operation also makes them unsuitable for toxic, flammable, or environmentally hazardous liquids.
Environmental Impact
Gland packing, due to the inherent leakage, can release process fluids to the environment. This is a concern with hazardous or environmentally harmful media.
The near-zero emission sealing of mechanical seals aligns well with stringent environmental regulations and the drive to minimize leaks and waste. Reduced leakage also means less product loss and contamination.
Material
Gland packing is typically made from soft, flexible yarns that are woven or braided. Common materials include PTFE, graphite, aramid fibers, and various synthetic fibers. Lubricants or blockers may be incorporated.
Mechanical seals utilize a combination of hard and soft materials. The sealing faces are made from rigid, wear-resistant materials like silicon carbide, tungsten carbide, or carbon graphite. Secondary seals use elastomers like FKM, EPDM, or PTFE.
Applications
Gland packing seals are often used in lower pressure, lower speed, and less critical applications. They are common in pumps, valves, and other rotating equipment.
Mechanical seals are used in more demanding applications where leakage control is critical, such as high-pressure pumps, refineries, chemical processing, and pharmaceutical manufacturing.