High-speed mechanical seals are critical components in rotating equipment that operate under demanding conditions. These specialized seals are designed to withstand extreme pressures, temperatures, and rotational speeds while effectively preventing leakage and ensuring reliable performance.
In this blog post, we will delve into the intricacies of high-speed mechanical seals, exploring their unique characteristics, design considerations, advantages, disadvantages, and diverse applications across various industries.

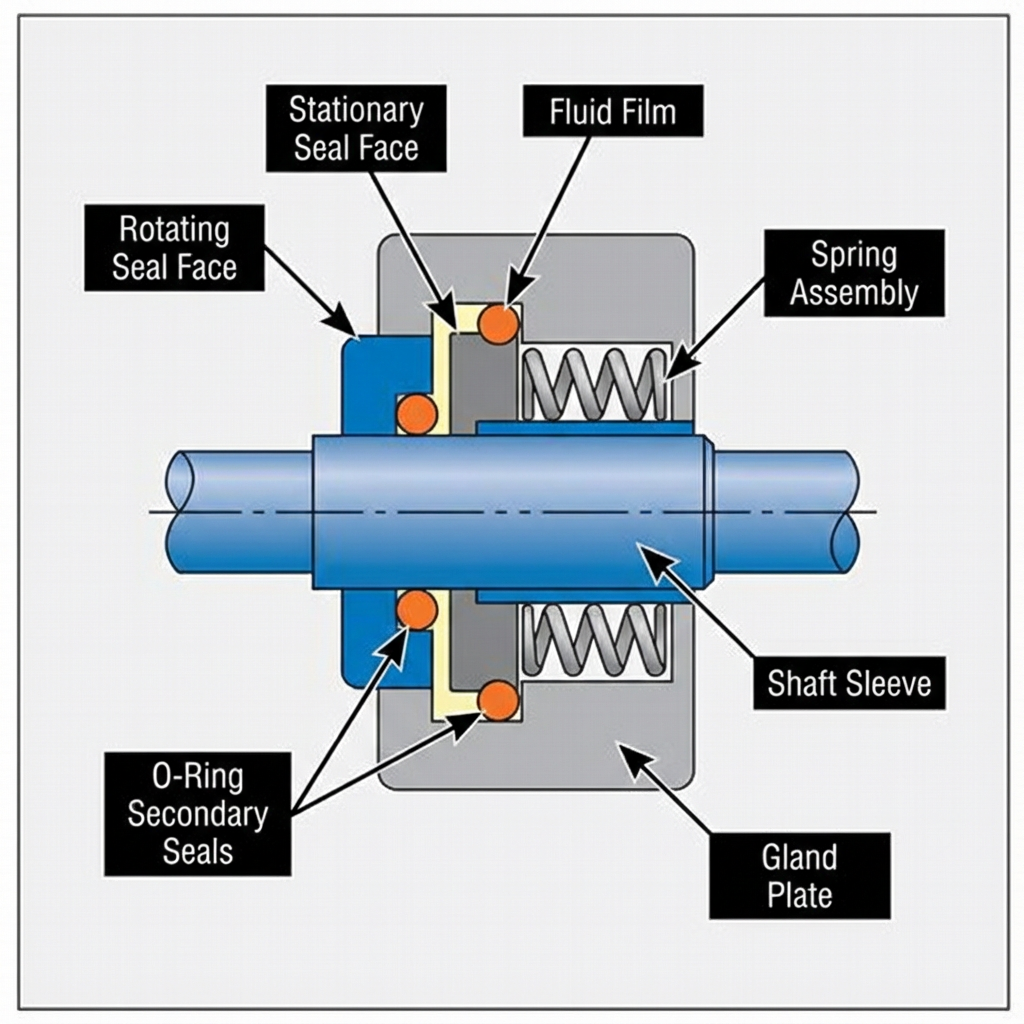
What Is a High-Speed Mechanical Seal
A high-speed mechanical seal is a critical component used in rotating equipment to prevent leakage of fluids or gases while operating at elevated speeds. These seals are designed to withstand the unique challenges associated with high-speed applications, such as increased friction, heat generation, and dynamic forces.
Characteristics of High-Speed Mechanical Seals
High-speed mechanical seals possess several distinct characteristics that enable them to perform effectively in demanding high-speed environments:
Structural Design
The structural design of high-speed mechanical seals is optimized to minimize heat generation and maintain stability at elevated speeds. Key design features often include:
- Balanced seal faces to evenly distribute pressure and reduce friction
- Precise face geometry to maintain a thin fluid film between the faces
- Robust construction to withstand high dynamic forces and vibration
Material Selection
Materials used in high-speed mechanical seals are carefully selected to withstand the rigors of high-speed operation. Common materials include:
- Silicon carbide
- Tungsten carbide
- Carbon graphite
- Engineered ceramics
- Specialized high-performance polymers
These materials offer excellent wear resistance, thermal conductivity, and chemical compatibility to ensure long seal life and reliability.
Precision Requirements
High-speed mechanical seals require extremely tight tolerances and precise manufacturing to function effectively. Key precision requirements include:
- Flatness and parallelism of seal faces
- Smooth surface finishes to minimize friction and wear
- Tight clearances between rotating and stationary components
- Accurate alignment of seal components
How High-Speed Mechanical Seals Work
High-speed mechanical seals operate by creating a thin fluid film between the rotating and stationary seal faces. This fluid film, often just a few microns thick, prevents direct contact between the faces and minimizes friction and wear.
As the shaft rotates, the fluid is drawn into the gap between the seal faces by viscous shear forces. The fluid film generates hydrodynamic pressure, which helps to keep the faces separated and maintain the seal.
To ensure efficient operation, high-speed mechanical seals incorporate features such as precision face geometry, specialized face materials, and advanced sealing aids like grooves or micro-surface textures. These elements work together to optimize fluid film formation and maintain seal integrity across a wide range of speeds and operating conditions.

Design Considerations for High-Speed Mechanical Seals
Pressure
High-speed mechanical seals must withstand significant pressure forces due to the high rotational speeds involved. The seal faces must maintain proper contact and alignment to prevent leakage and excessive wear. Designers must carefully consider the pressure ratings of the seal materials and ensure that the seal geometry can adequately distribute and balance the pressure forces across the sealing interface.
Temperature
The high rotational speeds of high-speed mechanical seals generate substantial amounts of heat due to friction between the seal faces. This heat can lead to thermal distortion, material degradation, and changes in fluid properties. Designers must select seal materials with appropriate thermal conductivity and thermal expansion coefficients to minimize the effects of temperature on seal performance. Proper cooling and lubrication systems may also be necessary to dissipate heat and maintain stable operating temperatures.
Speed
The rotational speed of the shaft directly impacts the performance and life of high-speed mechanical seals. As the speed increases, so do the centrifugal forces acting on the seal components, which can cause distortion, vibration, and instability. Designers must carefully consider the speed limits of the chosen seal materials and design the seal geometry to minimize the effects of centrifugal forces.
Medium Properties
The properties of the fluid being sealed, such as viscosity, compressibility, and chemical compatibility, play a significant role in the design of high-speed mechanical seals. The seal materials must be compatible with the fluid to prevent corrosion, swelling, or degradation. The fluid’s lubricating properties also affect the friction and wear characteristics of the seal faces. Designers must select seal materials and geometries that are suitable for the specific medium being sealed and consider factors such as fluid shear, cavitation, and entrained solids.
Shaft Vibration
High-speed mechanical seals are sensitive to shaft vibration, which can cause seal face misalignment, uneven wear, and leakage. Designers must consider the potential sources of vibration, such as shaft imbalance, misalignment, or resonance, and design the seal to minimize their effects. This may involve incorporating vibration-damping elements, such as O-rings or spring-loaded components, or specifying strict tolerances for shaft straightness and concentricity.
Runout
Shaft runout, or the deviation of the shaft from its true rotational axis, can cause cyclic loading and uneven wear on the seal faces of high-speed mechanical seals. Designers must specify tight runout tolerances for the shaft and seal components to minimize the effects of runout. This may involve precision machining, dynamic balancing, or the use of runout-compensating seal designs, such as floating or flexibly mounted seal faces.
Auxiliary Systems
High-speed mechanical seals often require auxiliary systems to ensure proper operation and longevity. These systems may include lubrication systems to provide a thin film of fluid between the seal faces, cooling systems to dissipate heat, and barrier fluid systems to isolate the sealed fluid from the atmosphere. Designers must carefully integrate these auxiliary systems into the overall seal design, considering factors such as flow rates, pressures, and compatibility with the sealed fluid.
Seal Chamber Dimensions
The dimensions and geometry of the seal chamber can significantly influence the performance of high-speed mechanical seals. Designers must ensure that the seal chamber provides adequate space for the seal components, allows for proper fluid circulation and heat dissipation, and minimizes turbulence and dead zones. The seal chamber should also be designed to facilitate easy installation, maintenance, and replacement of the seal components.
Here is the content for the requested section on the advantages, disadvantages, and applications of high-speed mechanical seals:
Advantages of High-Speed Mechanical Seals
Enhanced Sealing Performance
High-speed mechanical seals offer superior sealing performance compared to traditional sealing solutions. Their precision design and high-quality materials enable them to maintain a tight seal even under demanding high-speed operating conditions. This enhanced sealing capability minimizes leakage and prevents contamination of the sealed fluid or the surrounding environment.
Increased Reliability and Durability
The robust construction and advanced material selection of high-speed mechanical seals contribute to their exceptional reliability and durability. These seals are engineered to withstand the stresses and wear associated with high rotational speeds. With proper installation and maintenance, high-speed mechanical seals can provide extended service life, reducing the frequency of seal replacements and minimizing downtime.
Improved Energy Efficiency
High-speed mechanical seals are designed to minimize frictional losses, which translates to improved energy efficiency. The optimized geometry and precise clearances of these seals reduce drag and heat generation, resulting in lower power consumption. This energy efficiency benefit is particularly significant in high-speed applications where even small improvements can yield substantial energy savings over time.
Versatility and Customization
High-speed mechanical seals offer a high degree of versatility and customization options. They can be tailored to suit specific application requirements, including operating speeds, pressures, temperatures, and fluid compatibility. This adaptability allows for optimal sealing solutions across a wide range of industries and equipment types.
Disadvantages of High-Speed Mechanical Seals
Higher Initial Cost
One of the main drawbacks of high-speed mechanical seals is their higher initial cost compared to traditional sealing options. The precision manufacturing, advanced materials, and specialized design features required for high-speed operation contribute to the increased upfront investment. However, the long-term benefits of improved performance and reliability often justify the initial cost.
Increased Complexity
High-speed mechanical seals are more complex than standard mechanical seals. They require careful design consideration, precise installation, and proper operating conditions to function effectively. This complexity necessitates skilled personnel for installation, commissioning, and maintenance. Inadequate understanding or improper handling of high-speed seals can lead to premature failure or suboptimal performance.
Sensitivity to Operating Conditions
High-speed mechanical seals are more sensitive to operating conditions compared to other sealing solutions. Factors such as shaft misalignment, vibration, and thermal expansion can have a more pronounced impact on seal performance at high speeds. Maintaining stable and well-controlled operating conditions is crucial for the reliable operation of high-speed seals.
Limited Application Range
While high-speed mechanical seals offer versatility, they may not be suitable for all applications. Extremely high speeds, aggressive media, or severe temperature extremes can exceed the capabilities of even the most advanced high-speed seals. In such cases, alternative sealing technologies or modifications to the sealing system may be necessary.
Applications of High-Speed Mechanical Seals
Turbomachinery
High-speed mechanical seals find extensive use in turbomachinery applications, such as compressors, turbines, and pumps. These seals are critical for preventing leakage and maintaining efficiency in high-speed rotating equipment. They are designed to withstand the demanding conditions of high rotational speeds, pressures, and temperatures commonly encountered in turbomachinery.
Automotive and Aerospace Industries
The automotive and aerospace industries rely on high-speed mechanical seals in various applications. In automotive turbochargers and superchargers, these seals ensure reliable operation and prevent oil leakage under high-speed conditions. In aircraft engines and auxiliary power units, high-speed seals play a vital role in maintaining the integrity of lubrication and fuel systems.
Chemical and Petrochemical Processing
High-speed mechanical seals are employed in chemical and petrochemical processing equipment, such as reactors, mixers, and centrifuges. These seals provide reliable sealing performance in the presence of aggressive chemicals and demanding process conditions. They help prevent product contamination, ensure process safety, and minimize environmental impact.
Power Generation
In power generation applications, high-speed mechanical seals are used in steam turbines, generators, and auxiliary equipment. These seals are critical for maintaining the efficiency and reliability of power generation systems. They prevent steam leakage, reduce energy losses, and contribute to the overall performance and longevity of the equipment.